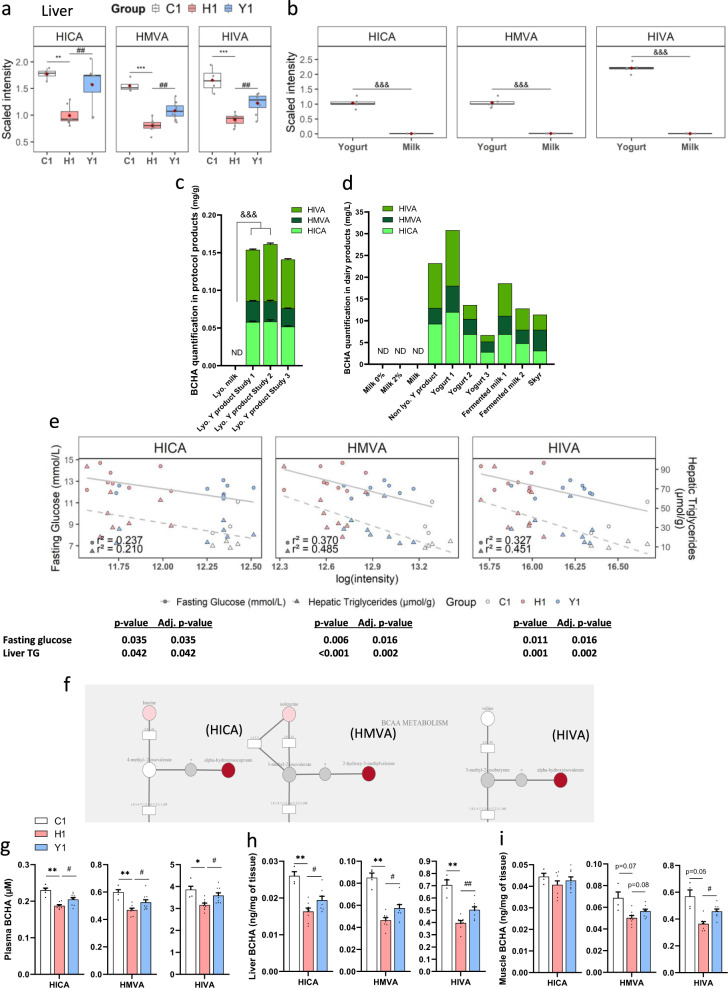
Fig. 4. Yogurt intake increases levels of branched-chain hydroxy acids (BCHA) in metabolic tissues of H-fed mice which correlates with metabolic benefits.
a Hepatic BCHA levels in Study 1: alpha-hydroxyisocaproate (HICA, lawn green), 2-hydroxy-3-methylvalerate (HMVA, dark green), and alpha-hydroxyisovalerate (HIVA, green) (HD4 UPLC-MS/MS, n = 4–8 mice). b BCHA levels in lyophilized yogurt and milk (HD4 UPLC-MS/MS, n = 5 productions). c BCHA content in lyophilized milk and yogurts used in all studies (targeted NMR, n = 5 productions in Study 1 and 2, n = 1 in Study 3, average of 5 replicates). d BCHA content in various dairy products (targeted NMR, n = 1, average of 5 replicates unless indicated otherwise). e Pearson correlations between hepatic BCHA levels and fasting glucose (solid gray line) and hepatic triglycerides (dash gray line). n = 4–8. P-value and adjusted p-value indicated. f BCHA metabolic pathway. BCAA are metabolized by EC 2.6.1.42 to oxo-acids and then by EC 1.2.4.4; EC 1.8.1.4 and EC 2.3.1.168 complex. Circles: metabolites; rectangles: enzymes. Red: p ≤ 0.05 between H1 and Y1; pink: 0.05 < p < 0.10. g–i BCHA content in g plasma, h liver and i muscle (targeted LC‐MS/MS, n = 4–5 in C and 8–9 mice in H, Y groups). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. a, b Thick black line is median, box spans from Q1 (25th percentile) to Q3 (75th percentile), whiskers extend to the most extreme observation within 1.5 times the interquartile range (Q3–Q1) from the nearest quartile. Data are scaled such that the median value measured across all samples was set to 1.0. Outliers-dots outside the whiskers of the plot. H vs C: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Y vs H: #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01. Lyophilized milk vs lyophilized yogurts products used in studies: &&&p < 0.001. H1 versus C1: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Y1 vs H1: #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01. Lyophilized yogurt products vs milk: §§§p < 0.001. C: low-fat low-sucrose control diet (C1: white); H: high-fat high-sucrose diet with a protein mixture replacing casein (H1: pink); L.: Lactobacillus; Lc.: Lactococcus; ND: non detected; S.: Streptococcus; Y: lyophilized yogurt incorporated in H diet (Y1: light blue). Number (1) refers to the study affiliation. a ANOVA, b, g–i T-tests, e Pearson correlations. Benjamini–Hochberg correction for multiple testing within each BCHA (e) or within tissues (g–i). FDR (q-value) correction for multiple testing over all tested metabolites (a, b). All tests were two-sided.