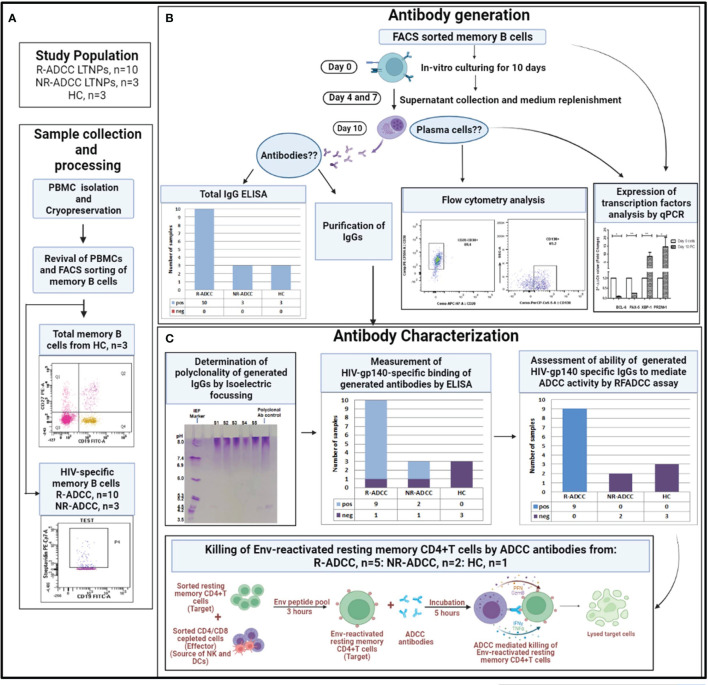
Figure 1.
Summary of the experimental workflow of the study. (A) Whole blood samples were collected from long-term non-progressors (LTNPs) with and without plasma antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) activity (R-ADCC, n = 10 and NR-ADCC, n = 3, respectively) and 3 healthy individuals (HCs) and processed for the separation and cryopreservation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). The PBMCs were then revived and memory B cells from three HCs and HIV-specific memory B cells from R-ADCC (n = 10) and NR-ADCC LTNPs (n = 3) were FACS sorted. (B) Antibody generation: the FACS-sorted memory B cells from all the samples were cultured for 10 days. On day 10, supernatants were assessed for the presence of antibodies and were then column purified. The cells were assessed for the differentiation into plasma cells by flow cytometry and real-time PCR analysis at day 10. (C) Antibody characterization: the generated antibodies were then assessed for the presence of gp140 antibodies using ELISA, their ability to mediate ADCC using rapid fluorometric antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (RF-ADCC) assay, and their ability to facilitate NK cell-mediated lysis of Env-reactivated latent reservoirs using a flow-based latency reduction assay as reported earlier (16).