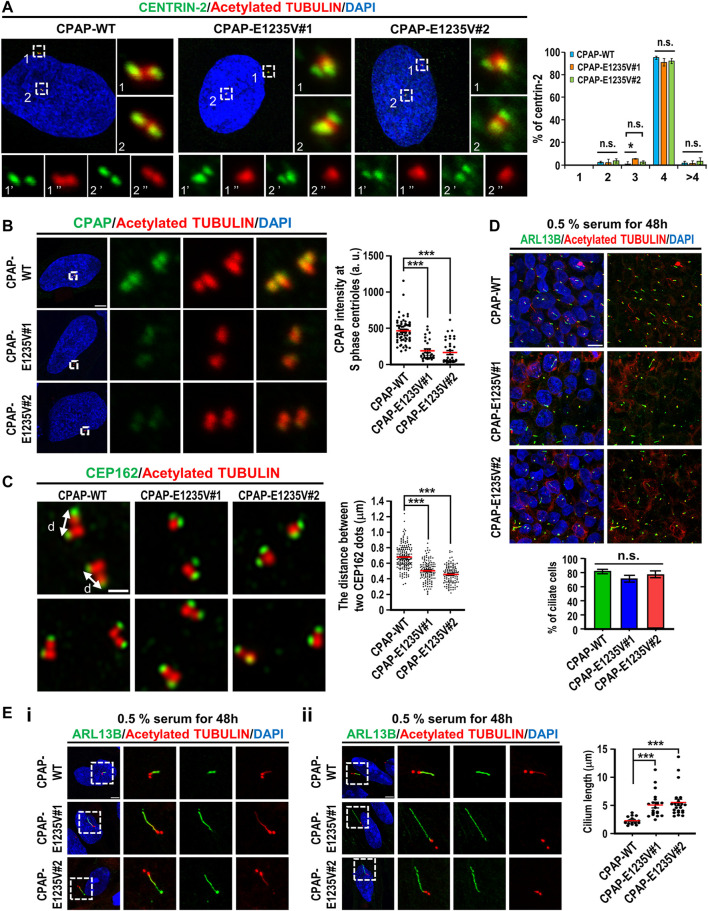
FIGURE 3.
hiPSCs carrying CPAP-E1235V mutation displayed short centrioles and abnormally long cilia. Cells were synchronized at early S phase by treating aphidicolin (2 μg/ml) for 24 h (S phase) and released in fresh culture medium without aphidicolin for another 16 h (G2 phase). (A) Centriole numbers in control and two hiPSC mutant clones. Cells in the G2 phase were immunostained with antibodies against CENTRIN-2 (a centriole marker) and Acetylated-TUBULIN (Ac-TUB) (left) and the number of centriole was quantified (right) from three independent experiments. (B) Immunostaining and quantification of CPAP signals in S phase centrioles. n = 61 for CPAP-WT; n = 30 for CPAP-E1235V#1; n = 37 for CPAP-E1235V#2. (C) Airyscan images of centriole lengths by measuring the distance between two CEP162 dots in each pair of centrioles. n = 192 for CPAP-WT; n = 134 for CPAP-E1235V#1; n = 122 for CPAP-E1235V#2. (D,E) Immunostaining of CPAP-WT and mutant cells with antibodies against ARL13B (a ciliary membrane marker) and Ac-TUB (a centriole and ciliary axoneme marker). The cells were treated with 0.5% low serum starvation for 48 h. (D) The number of ciliated cells. n = 265 for CPAP-WT; n = 95 for CPAP-E1235V#1; n = 196 for CPAP-E1235V#2. Data are presented as the mean ±SEM from a pool of n cells from three independent experiments. (E) Quantification of ciliary length. n = 20 for CPAP-WT; n = 20 for CPAP-E1235V#1; n = 22 for CPAP-E1235V#2. Two types of long cilia were observed in the mutant cells. One type of long cilia displays long ciliary membranes (ARL13B+) and long ciliary axonemes (Ac-TUB+) (Ei), while the other type of cilia exhibit long ciliary membranes (ARL13B+) but short axonemes (Ac-TUB+) (Eii). Data are presented as the mean ±SEM. ***p < 0.001. Scale bar: 5 μm in (A,B,E), 0.5 μm in (C), 10 μm in (D).