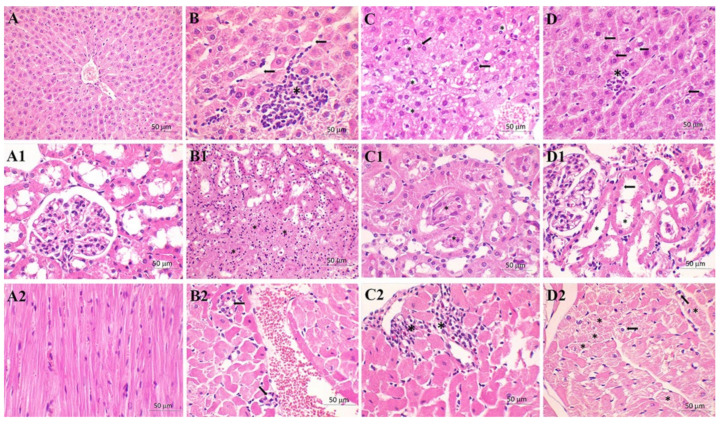
Figure 2.
Tissue histology analysis (H&E stain, 400×). Liver: (A) control (C) group—normal histological structure of the hepatic tissue; (B) sepsis (S) group—larger zone of centrilobular necrosis (asterisk) with sinusoidal dilatation (arrow); (C) sepsis (S) group—hydropic degeneration (vacuolization of the hepatocytes cytoplasm, asterisk) and binucleation of hepatocytes (usually seen in regenerating cells, arrow); (D) meldoniuM + Sepsis (M + S) group—rare spotty necrosis (asterisk), several adjacent hepatocytes are absent and replaced by inflammatory cells and focal steatosis in the surrounding preserved hepatocytes (arrow). Kidney: (A1) control (C) group—normal histological structure of the renal tissue; (B1) sepsis (S) group—severe tubular necrosis with complete loss of parenchymal architecture (asterisk); (C1) sepsis (S) group—intratubular obstruction due to the denuded epithelium and cellular debris and bleb formation (asterisk); (D1) meldonium + sepsis (M + S) group—absence or thinning of brush-border of the proximal tubule (arrow) with dilated proximal tubule (asterisk) with flattening of tubular epithelium. Heart: (A2) control (C) group—normal histological structure of the heart tissue; (B2) sepsis (S) group—Focal inflammatory cell infiltration (arrow) in the myocardium, consisting of mononuclear cells, occasionally occurs. This change is sometimes accompanied by slight myocardial necrosis; (C2) meldonium + sepsis (M + S) group—diffuse interstitial mononuclear infiltration (asterisk) with greater loss of myocytes; (D2) meldonium + sepsis (M + S) group—intracellular vacuolization (arrow) and a loss of cross-striations (asterisk) in subendocardial zone of heart.