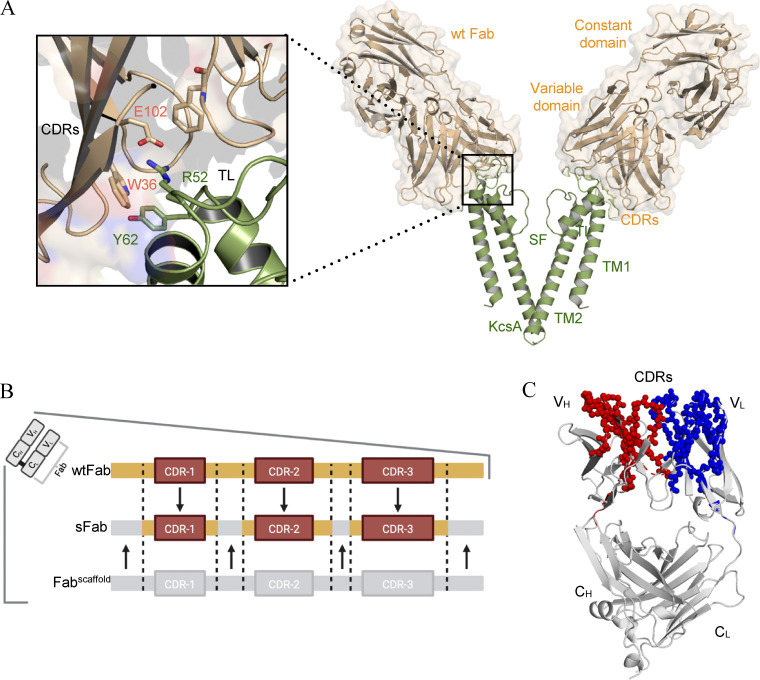
Figure 1.
Structural analysis of the wtFab–KcsA crystal structure. (A) Side view (right) of only two diagonally opposing monomers of KcsA for clarity (green), showing the transmembrane helices (TM1, TM2), selectivity filter (SF), and the wtFab (gold) interacting near the turret loop (TL). A closeup view of the interaction interface (left) showing the interaction of the CDRs with residues in the TL; the crystal structure is obtained from PDB accession no. 1K4C. (B) Design of the sFab based on the human Herceptin Fab scaffold (Fabscaffold) showing the heavy and/or light CDRs (orange) necessary for restoring binding to KcsA. (C) ROSETTA homology modeling of the sFab (gray). Amino acid residues of high similarity with wtFab are shown as spheres in red and blue for variable heavy (VH) and light (VL) domains, respectively.