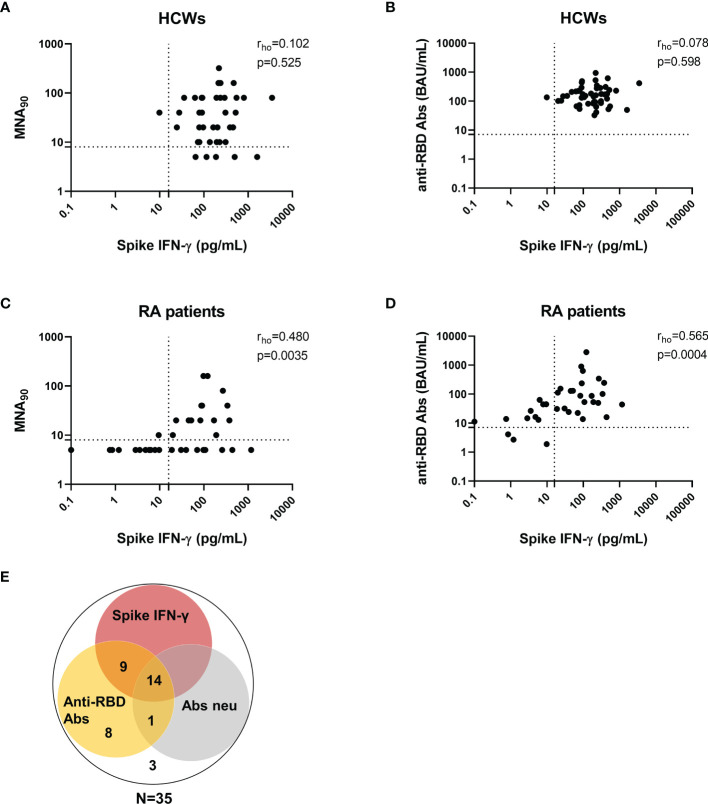
Figure 7.
Correlation between T-cell response and anti-RBD or neutralizing antibodies in HCWs and RA patients. Correlation between neutralizing antibodies and the IFN-γ-spike-specific T-cell response in HCWs (A) and RA subjects (C). Correlation between anti-RBD antibodies and the IFN-γ-spike-specific T-cell response in HCWs (B) and RA subjects (D). Anti-RBD and neutralizing antibodies were quantified in serum samples and expressed as binding antibody units (BAU)/ml and reciprocal of dilution (MNA90), respectively. T-cell response to spike antigen was assessed by measuring IFN-γ levels and reported after subtracting the background. Dashed lines identify the cutoff of each test (anti-RBD: 7.1 BAU/ml; MNA90: 8 and spike: 16 pg/ml). Correlation between assays was assessed by non-parametric Spearman’s rank test (p < 0.05). (E) Venn diagram shows positive results with anti-RBD IgG, neutralizing antibodies and IFN-γ T-cell response. RA, rheumatoid arthritis; RBD, receptor-binding domain; HCWs, health care workers.