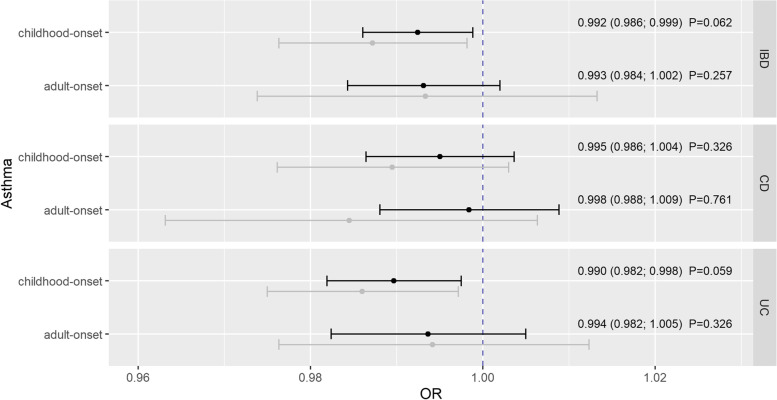
Fig. 2.
Estimates given as odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals for the effect of childhood- and adult-onset asthma on peptic ulcer disease (PUD), gastroesophageal reflux disease (GORD), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Estimates were derived by the multiplicative random effects inverse-variance weighted method (except the effect of adult-onset asthma on ulcerative colitis that was estimated by the Wald atio approach). Reported P-values were adjusted for multiple testing using the Benjamini-Hochberg procedure. Gray estimates represent the results before and black estimates the results after outlier-removal. IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; CD, Crohn’s disease; UC, ulcerative colitis