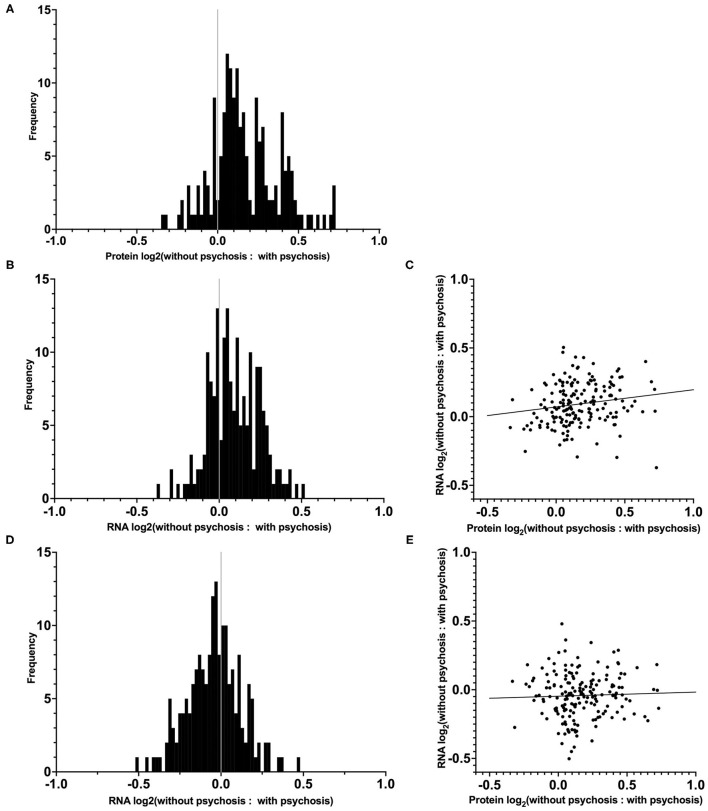
Figure 2.
Distribution and correlation of synaptic transcript and protein levels in AD–P relative to AD+P subjects. (A) Distributions of log2 ratios are shown for 180 synaptic proteins (19) for which corresponding mRNA levels were quantified in the current study. (B) Distribution of RNA expression ratios of the 180 synaptic genes identified in our DE analysis, prior to cell type proportion adjustments. The proportion of synaptic transcripts upregulated in AD–P compared to AD+P was 69.4%, compared to 49.6% of non-synaptic transcripts (Chi-square test, p = 3.874E-7). (C) Correlation between the 180 synaptic protein and transcript expression ratios (AD–P: AD+P, spearman's rho = 0.2257, p = 0.0024). (D) Analysis of the same synaptic transcripts as in (B), accounting for the contribution of cell type proportions as covariates, eliminates their upregulation in AD–P. (E) Inclusion of cell type proportions as covariates in analysis of synaptic transcripts similarly abolishes the correlation between synaptic transcript and protein levels (spearman's rho = 0.0302, p = 0.6868).