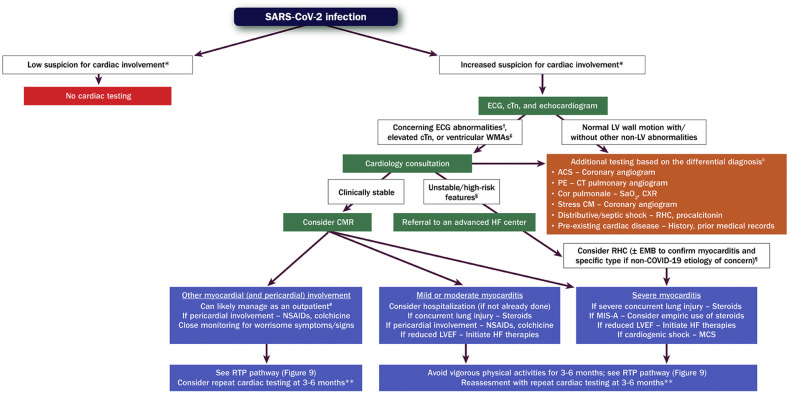
Figure 3.
Evaluation and Management of Patients With Suspected Myocarditis or Myocardial Involvement
Green boxes = cardiac testing for evaluation of myocarditis/myocardial involvement. Orange box = other cardiac/noncardiac testing. Purple boxes = management. ∗Informed by symptoms suggestive of cardiac involvement, including chest pain/pressure, dyspnea, palpitations, and syncope. †Includes diffuse T-wave inversion, ST-segment elevation without reciprocal ST-segment depression, and prolongation of the QRS complex duration. ‡Often in a noncoronary distribution; may also include abnormal ventricular strain. §Includes hypotension, cardiogenic shock, sustained ventricular arrhythmias, and/or advanced atrioventricular block. ‖This is an incomplete list of potential etiologies. ¶Testing for viral genomes should be performed on frozen heart tissue to exclude other causes of myocarditis, if possible. #Assumes chest pain is the only symptom, LV systolic function is preserved, and there are no ventricular arrhythmias. ∗∗Includes an ECG, echocardiogram, ambulatory rhythm monitor, and CMR. ACS = acute coronary syndrome; CM = cardiomyopathy; CMR = cardiac magnetic resonance imaging; COVID-19 = novel coronavirus disease 2019; CT = computed tomography; cTn = cardiac troponin; CXR = chest X-ray; ECG = electrocardiogram; EMB = endomyocardial biopsy; HF = heart failure; LV = left ventricular; LVEF = left ventricular ejection fraction; MCS = mechanical circulatory support; MIS-A = multisystem inflammatory syndrome in adults; NSAIDs = nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; PE = pulmonary embolism; RHC = right heart catheterization; SaO2 = arterial oxygen saturation; SARS-CoV-2 = severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; WMAs = wall motion abnormalities.