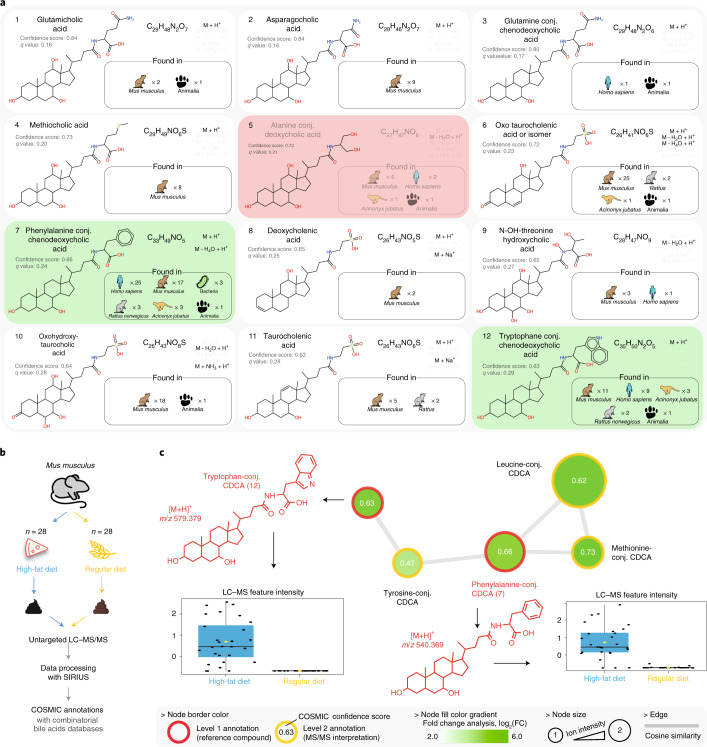
Fig. 6. Applying COSMIC to discover novel bile acid conjugates in a mice fecal dataset.
a, Top 12 highest-scoring COSMIC annotations of ‘truly novel’ bile acid conjugates. Bile acid conjugates that are also present in PubChem are omitted from the list; see Supplementary Table 2 for the complete list. For each bile acid conjugate, we report its chemical name, putative structure, molecular formula and adducts of annotations for this structure. In addition, we report confidence scores and estimated q values; note that the exact FDR is 0% for the top 4 bile acid conjugates and 8.3% for the top 12 (compare to Extended Data Fig. 5). We also report species and number of datasets with spectral matches from a MASST search. Two annotations verified by authentic standards are highlighted in green and the single incorrect annotation in red. b, Experimental design and the data processing and annotation carried out with COSMIC. c, MS-based molecular network of novel bile acid conjugates annotated with COSMIC and the combinatorial bile acids structure database. Two annotations (7 and 12) were validated using synthetic standards, and the other annotations were manually inspected. Fold change analysis showed that all these bile acid derivatives were predominantly observed in mice fed an HFD. Box plots depict the first and third quartiles as well as the median. Whiskers extend to the smallest and largest value but no further than 1.5× interquartile range from the hinges. n = 56 independent biological experiments. conj., conjugate; FC, fold change.