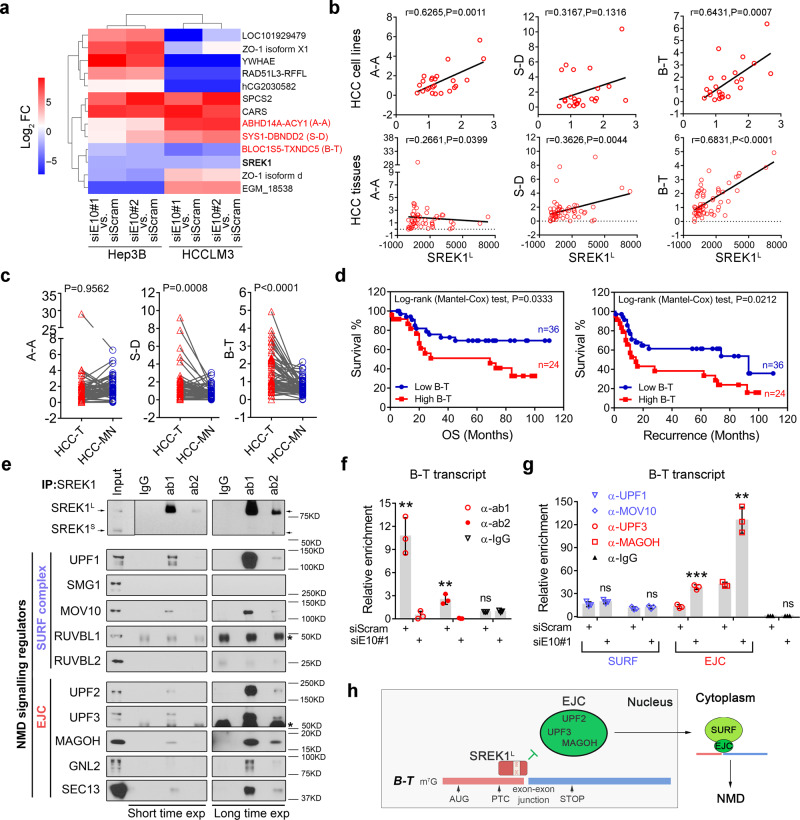
Fig. 3. SREK1L maintains the expression of B-T, an NMD target, via inhibiting the exon-exon junction complex binding to the B-T transcript.
a Expression heat map of scramble (siScram)-transfected or SREK1L -knockdown (siE10#1 or #2) HCC cell lines mediated by siRNA. Targeted NMD genes are labeled in red. b Pearson correlation assay to assess the expression of three NMD target genes and SREK1L in 24 HCC cell lines or 60 HCC tumor tissues. c The expression of three NMD target genes in 60 tumor (T) and matched normal (MN) tissues, two-tailed, paired t test is used. d Analysis of OS and disease-free survival in 60 HCC patients with either high or low B-T expression. e Endogenous immunoprecipitation of SREK1-associated components from the SURF or EJC complex in Hep3B cells using IgG or two commercial antibodies against SREK1 (ab1: recognizing SREK1L, ab2: recognizing both L and S forms of SREK1). The star symbols indicate the heavy chain. The RNA immunoprecipitation assay for the detection of the enrichment of f SREK1, or the components of NMD complexes g UPF1, MOV10, UPF3, MAGOH on the B-T transcript in scram control or SREK1L knockdown Hep3B cells (n = 3, biologically independent experiments), data are shown as the mean ± SD, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. h A proposed potential regulatory model of SREK1L protecting B-T from NMD via inhibiting the EJC binding to B-T transcript in HCC cells. Two-tailed, unpaired t test is used for (b, f, g). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.