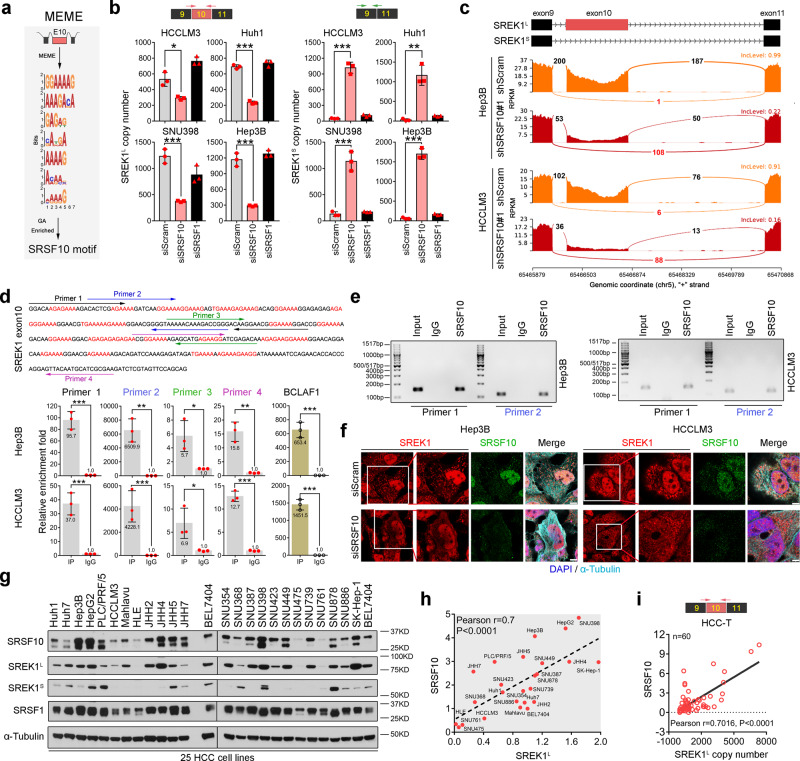
Fig. 5. SREK1L is a direct AS target of SRSF10 in HCC cells.
a Identification of the SRSF10-binding motif in the exon 10-coding mRNA region by MEME motif analysis. b Expression analysis to determine the copy numbers of two SREK1 variants, SREK1L and SREK1S, after SRSF10 or SRSF1 knockdown assays in four HCC cell lines (n = 3, mean ± SD). c Sashimi plots of exon 10 junction reads in stable SRSF10-knockdown or shScram-transfected cells. d Four sets of primers specific for the SREK1 exon 10 sequence (upper panel) were employed to detect exon 10 using real-time PCR (lower panel, n = 3, mean ± SD) and are labeled with different colors. e DNA gel detection of SREK1L binding in the RIP by SRSF10 or IgG in Hep3B or HCCLM3 cells. f Confocal microscopy of endogenous SREK1 (shown in red) and its colocalization with endogenous SRSF10 (stained with antibody against SRSF10, shown in green), microtubules (stained with antibody against α-tubulin, shown in purple) and nuclei (stained with DAPI, shown in blue) in siSRSF10- or siScram-transfected Hep3B and HCCLM3 cells, scale bar = 3 μm. g Immunoblot analysis of SRSF10, SRSF1, SREK1L and SREK1S in 25 HCC cell lines. Pearson correlation analysis of h the expression of SREK1L with SRSF10 protein expression in 25 HCC cell lines, and i the expression of SRSF10 with SREK1L in 60 HCC tumors (HCC-T) tissues. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001, two-tailed, unpaired t test is used for (b, d). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.