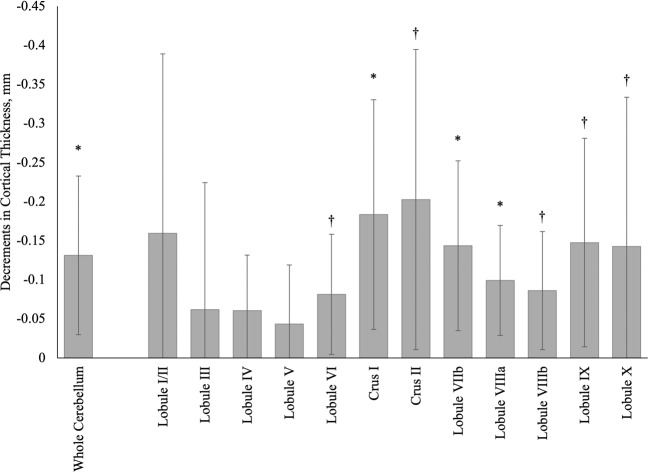
Fig. 2. Reductions in mean bilateral cortical thickness (mm) in the whole cerebellum and across 12 cerebellar regions of interest in World Trade Center responders with cognitive impairment (n = 48) when compared to WTC responders who were cognitively unimpaired (n = 51).
Confidence intervals are shown using error bars. Reductions with confidence intervals not crossing the base line were nominally significant, while those marked with * survived adjustment for the false discovery rate.