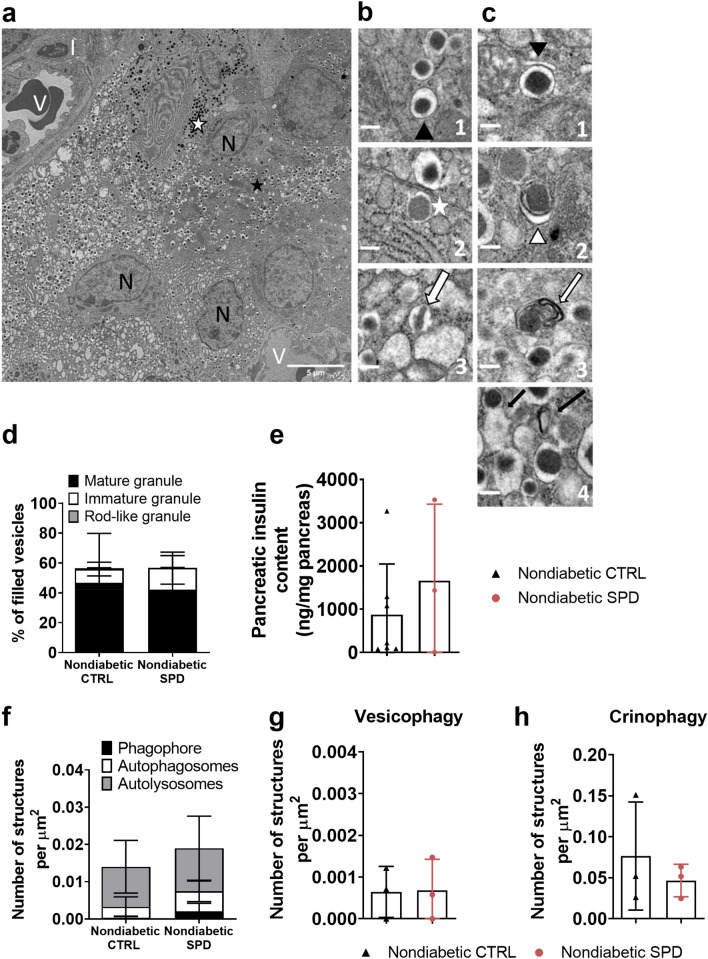
Figure 3.
Daily oral spermidine treatment did not alter insulin granule homeostasis in female nondiabetic mice. (a) A stitched micrograph including 25 single micrographs (V: vessel, N: nucleus, I: immune cell), scale bar: 5 µm. (b1) Black arrowhead indicates mature granules with a condensed core containing insulin. (b2) White asterisk marks immature transforming granules with a white halo. (b3) White arrow indicates rod-like insulin granules—crystallized structure surrounded by a bright halo, scale bar: 0.5 µm. (c1) Black arrowhead indicates a phagophore (dilated membrane) enwrapping a mature granule with a dark core. (c2) White arrowhead marks autophagosome (double bilayer) surrounding a mature granule. (c3) Autolysosome: white arrow indicates enclosed digested granule without a halo—membrane stacks within the autolysosome. (c4) Crinophagy: black arrows indicate a fusion of mature granules with electron-bright lysosomes, scale bar: 0.5 µm. (d) Insulin granule types normalized to filled vesicles. (e) pancreatic insulin content measured by ELISA (ctrl n = 7, spd n = 3). (f) Number of autophagy pathway structures (phagophore, autophagosome, autolysosome) per µ. (g) Number of vesicophagic vesicles per µm2. (h) Number of crinophagic vesicles per µ. Mice with blood glucose levels less than 200 mg/dl in two consecutive measurements were determined as nondiabetic at 35 weeks of age. Each datapoint represents the average of 3 islets from one mouse; area of 332 µ–2272 µ from each islet was analyzed. Nondiabetic ctrl mice (n = 3) and nondiabetic spd mice (n = 3). Data is shown as mean ± SD. Mann–Whitney U test was used as statistical analysis.