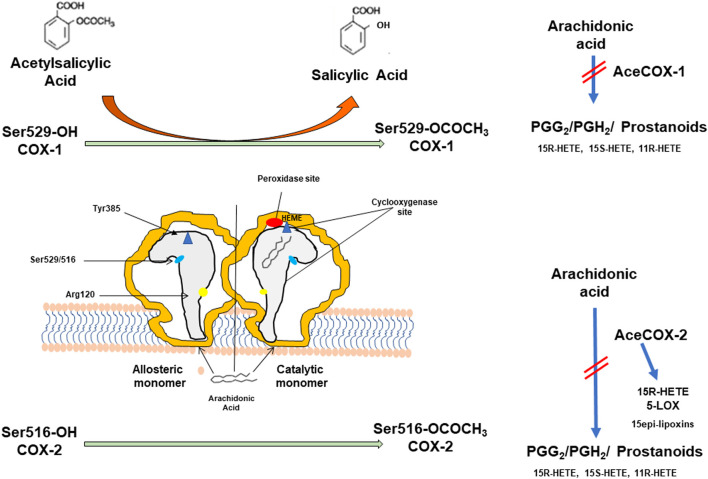
FIGURE 1.
Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid, ASA) acts by irreversibly acetylating cyclooxygenase (COX)-1 and COX-2. Prostaglandin H synthase (PGHS)-1 and -2 (also known as COX-1 and COX-2) are microsomal homodimeric heme glycoproteins that catalyze two key reactions in the biosynthesis of prostanoids: the bis-dioxygenation of arachidonic acid to form PGG2 (by the cyclooxygenase activity) and the reduction of PGG2 to PGH2 (by the peroxidase activity). In addition to PGH2, the monohydroxy acids 11(R)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid 11(R)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid 11R-(HETE), 15S-HETE, and 15R-HETE are generated as minor products of the cyclooxygenase reaction. COX-isozymes function as conformational heterodimers comprised of a regulatory allosteric monomer and a catalytic monomer. The catalytic monomer has a bound heme, whereas the allosteric monomer does not. The cyclooxygenase active site is a hydrophobic channel (reported in grey), and Arg-120 is located near its mouth. Arg-120 forms an ionic bond with the carboxylate group of arachidonate, and this interaction is an important contributor to the overall strength of arachidonate binding to COX-1 more than COX-2. Arg-120 is also the binding site for Aspirin. At the top of the channel is located Tyr-385, which is the critical catalytic amino acid for the cyclooxygenase reaction. Ser-529 and Ser-516 are the aminoacids acetylated by Aspirin. The acetylation of COX-isozymes is associated with the formation of salicylic acid, a weak COX inhibitor. The acetylation of only one monomer of COX dimer is sufficient for causing profound inhibition of cyclooxygenase activity. The acetylation of COX-1 at Ser-516 inhibits the catalytic activity of cyclooxygenase and prevents the generation of PGG2. In contrast, acetylated COX-2 at Ser-516 gains a novel catalytic activity and forms 15 R-HETE. 15R-HETE could be transformed to 15(R)epi-lipoxin (LX)A4 and 15epi-LXB4 in cells expressing the 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX), the enzyme also responsible for leukotriene biosynthesis.