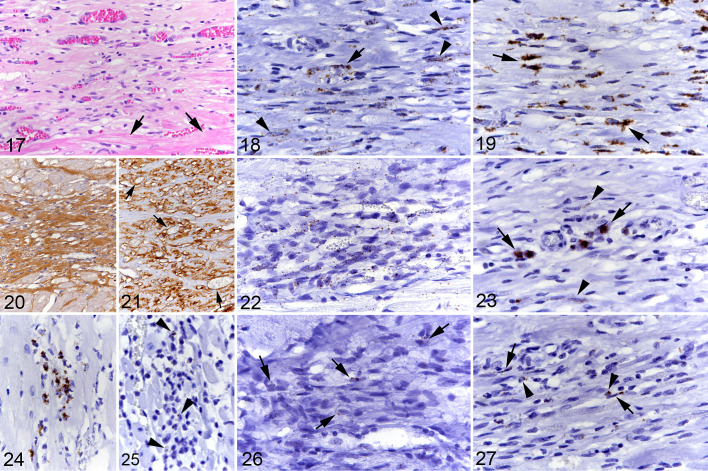
Figures 17–27.
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, left ventricular free wall, cat. Focal area of cell-rich fibrosis with abundant small and medium-sized vessels. Figure 17. Case 1. Focal area of cell- and vessel-rich fibrous connective tissue. Arrows: adjacent cardiomyocytes. Hematoxylin eosin (HE). Figure 18. Case 1. Numerous, predominantly spindle-shaped cells (arrowheads) as well as vascular endothelial cells (arrow) express CD34 mRNA. RNA-in situ hybridization (RNA-ISH). Figure 19. Case 1. There are numerous, mainly spindle-shaped cells with strong Col1A1 mRNA signal (arrows). RNA-ISH. Figure 20. Case 12. Area with lower cellularity exhibiting abundant collagen I deposition. Immunohistochemistry (IHC). Figure 21. Case 12. Collagen IV deposition is predominantly seen around vessels (arrows). IHC. Figure 22. Case 12. The majority of cells within the focal lesion exhibit a weak MEF2C mRNA signal. RNA-ISH. Figure 23. Case 1. Focal lesion with a few individual Kit mRNA positive round cells consistent with mast cells (arrows) and rare elongate cells with a weak signal (arrowheads). RNA-ISH. Figure 24. Case 1. Small cluster of CD14 mRNA positive round cells in the interstitium. RNA-ISH. Figure 25. Case 10. Rare individual round cells in the interstitium exhibit a weak CCR2 signal (arrowheads). RNA-ISH. Figure 26. Case 12. Several elongate to spindle-shaped cells in a focal area of cell-rich fibrosis exhibit a weak CD14 signal (arrows). RNA-ISH. Figure 27. Case 1. Several round cells (arrowheads) and spindle-shaped cells (arrows) in a focal area of cell-rich fibrosis exhibit a weak CCR2 signal. RNA-ISH.