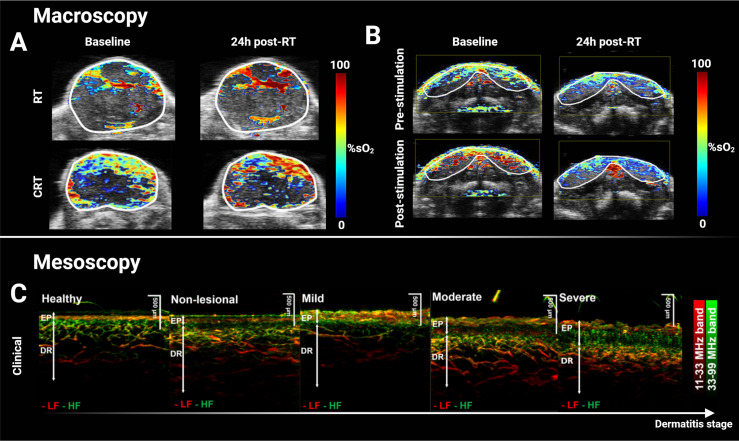
Figure 1.
Macroscopic and mesoscopic photoacoustic imaging can monitor treatment-induced vascular changes and disease stage. (A) Multispectral optoacoustic tomography (MSOT)-derived quantitative blood oxygen saturation map (sO2) overlaid on co-registered ultrasound axial slice of a head & neck patient-derived xenograft tumor before and after a single dose of 15 Gy (top panel), and before and after combined 7.5 Gy of radiotherapy and administration of chemotherapeutic cetuximab. Increased sO2 24h after treatment was associated with decreased tumor volume two weeks later. (B) Hemodynamic stimulation challenge of salivary glands before and after a single dose of 15 Gy with decreased change in sO2 response post-radiotherapy suggesting radiation-induced damage. (C) Clinical XZ maximal intensity projection of mesoscopic PAI of graded atopic dermatitis in human skin. Vascular and structural scoring could accurately grade dermatitis and such score could potentially be translated for grading radiation-induced toxicity in RT. Panels (A, B) adapted from Rich et al. (60), and panel (C) adapted from Yew et al. (61). EP, Epidermis; DR, Dermis; LF, low frequency; HF, high frequency; RT, radiotherapy; %sO2, percent blood oxygen saturation; CRT, chemoradiotherapy.