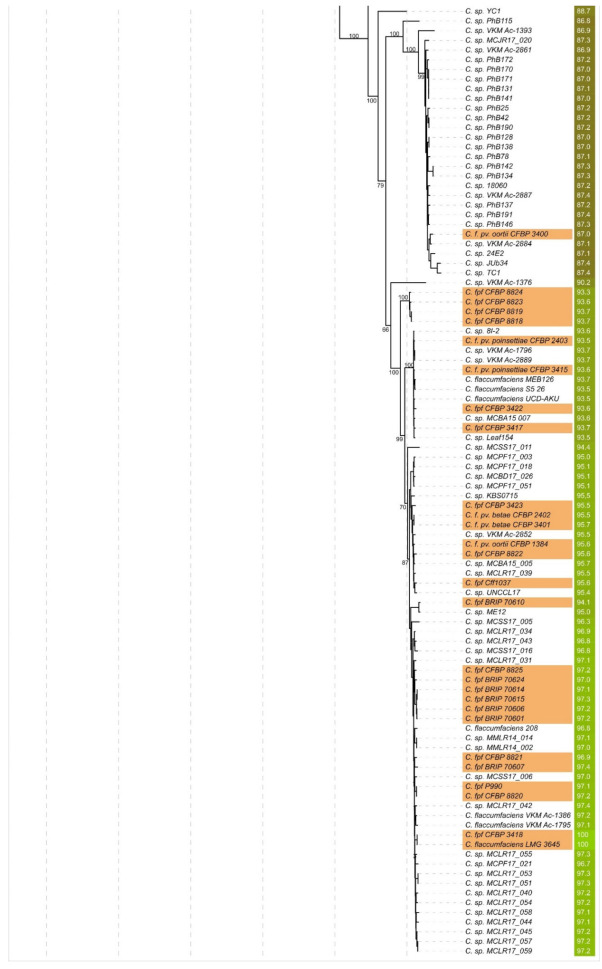
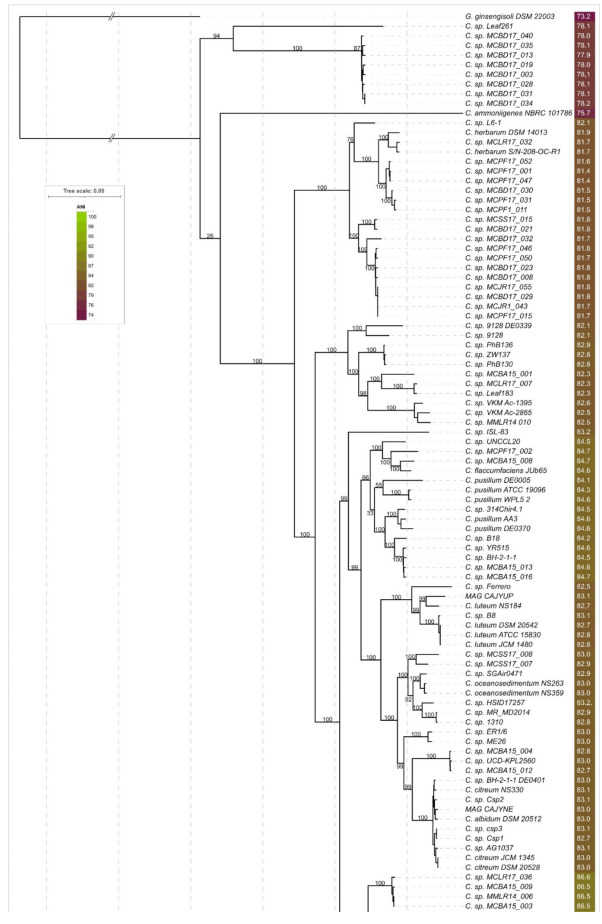
Figure 3.
Best-scoring phylogenetic trees obtained with RAxML using concatenated nucleotide sequences’ alignments of ribosomal proteins extracted from 190 Curtobacterium genomes and Gryllotalpicola ginnsengisoli DSM 22003. The abbreviations are as follows: C.—Curtobacterium, G.—Gryllotalpicola, C. f.—Curtobacterium flaccumfaciens, and C. fpf—flaccumfaciens pv. flaccumfaciens. The C. fpf strains with confirmed pathogenicity are coloured yellow-orange. ANI values compared to the C. fpf CFBP 3418-type strain are shown to the right of the organism’s name and coloured according to a heat map scale. Bootstrap support values are shown near the branches of the rectangular tree as a percentage of 1000 replicates. The scale bar shows 0.05 estimated substitutions per site and the tree was rooted to Gryllotalpicola ginnsengisoli DSM 22003.