Figure 4.
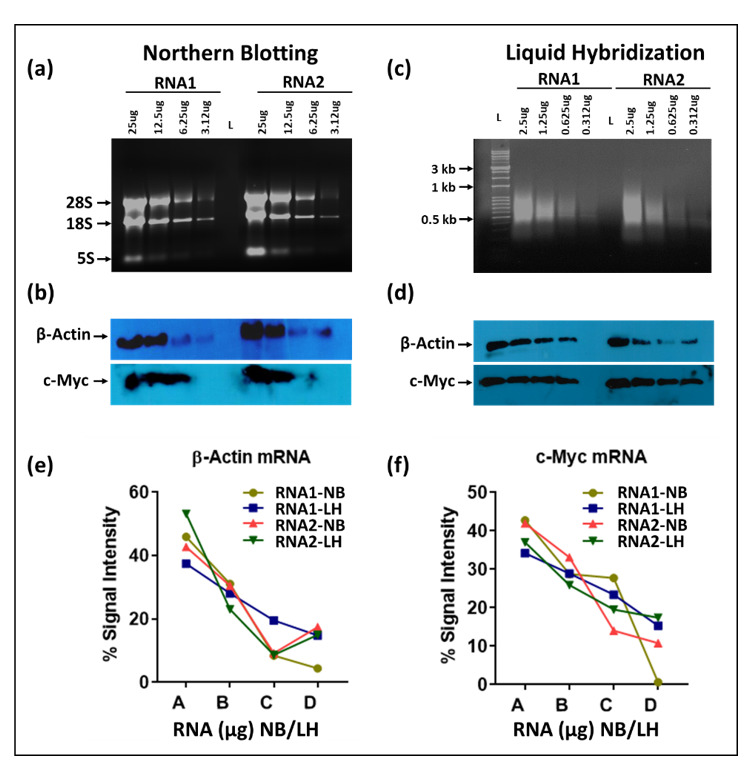
Comparative analysis of northern blots (NB) and liquid hybridization (LH) techniques. For northern blotting, serial dilutions of TRIzol-extracted RNA samples (25, 12.5, 6.25 and 3.125 μg each) were loaded onto a 1.2% denatured formaldehyde-agarose (FA) gels followed by semi-dry transfer to a nylon membrane and hybridization with biotinylated probes (50 pmol/mL). Whereas for liquid hybridization, serial dilutions of RNA samples (2.5, 1.25, 0.625 and 0.3125 μg each) were subjected to hybridization with the same amount of biotinylated probe (10 pmol/reaction) followed by Exonuclease I (Exo-I) treatment. After hybridization, the hybridized mixtures were loaded on non-denaturing agarose gels in MOPS buffer followed by transfer to a nylon membrane(s) using a semi-dry blot. After transfer, each membrane was UV crosslinked and EDC cross-linked for 2 hrs at 80 °C followed by incubation with HRP-conjugated streptavidin and detection using X-ray film. Ethidium bromide was added to the gels for visualization under UVP. (a) Gel image of ethidium-bromide-stained FA gels before transfer to a nylon membrane. (b) Northern blot showing expression levels of different mRNAs, including β-Actin and c-Myc after transfer to a nylon membrane and stripping. Images were taken using X-ray films. (c) UVP image of the hybridized RNA-probe mixture on a non-denaturing agarose gel before transfer. (d) Expression levels of selected mRNA(s) using X-ray film after transfer to nylon membranes. (e,f) Quantitative analysis of mRNAs expression levels after northern or liquid hybridization techniques. Image quantification was performed using GelQuant.NET software. Percent intensities were measured for each mRNA and plotted against the corresponding amount of RNA. X-axis labels: A = 25 or 2.5 μg; B = 12.5 or 1.25 μg; C = 6.25 or 0.625 μg; D = 3.125 or 0.3125 μg RNA).
