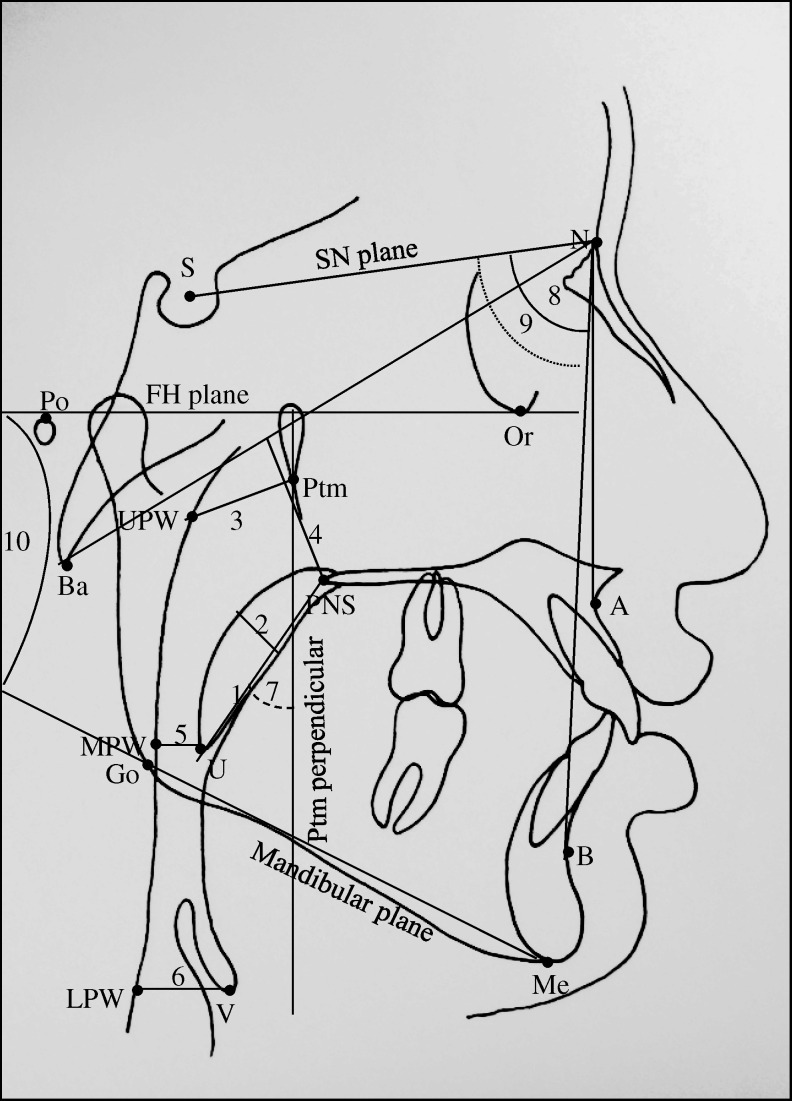
Figure 2.
Various cephalometric reference planes and linear and angular parameters used in the study. Reference planes: SN plane indicates the line joining ‘S’ and ‘N’; FH plane, line joining ‘Po’ and ‘Or’; Ptm perpendicular (Ptm per), perpendicular plane on FH plane at ‘Ptm’; and Ba-N plane, line joining ‘Ba’ and ‘N.’ Linear parameters: 1. SPL (U–PNS) indicates linear distance between U and PNS; 2. SPT, the maximum thickness of the soft palate; 3. DNP (Ptm–UPW), linear distance between ‘Ptm’ and ‘UPW’; 4. HNP, the shortest linear distance from PNS to Ba-N plane; 5. DOP (U–MPW), linear distance between ‘U’ and ‘MPW’; and 6. DHP (V–LPW), linear distance from ‘V’ to ‘LPW.’ Angular parameters: 7. SPI (Ptm per × PNS-U), the angle between Ptm perpendicular and soft palate (PNS-U); 8. SNA, angle between ‘S,’ ‘N,’ and ‘A’; it represents the antero-posterior position of the maxilla in relation to the anterior cranial base; 9. SNB, angle between ‘S,’ ‘N,’ and ‘B’; it represents the antero-posterior position of the maxilla in relation to the anterior cranial base; and 10. FMA, angle between FH plane and mandibular plane (Go-Me).