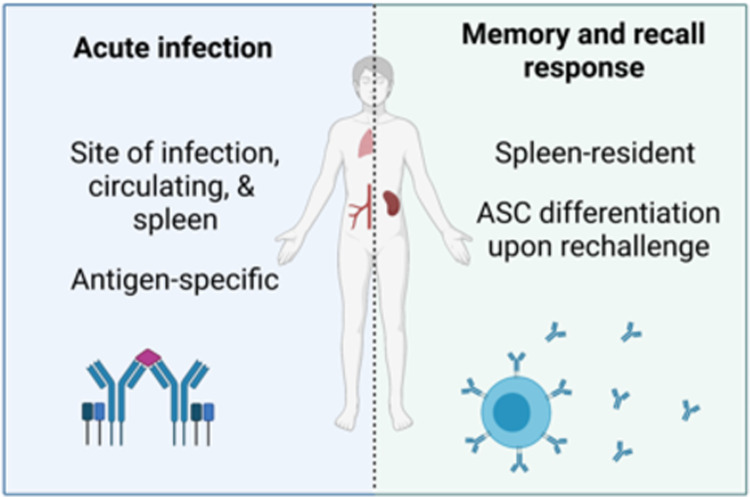
Fig 1. ABCs in acute infection and recall response.
During acute viral infection, ABCs are increased at the site of infection, in circulation, and in the spleen, and are largely antigen specific. Following clearance of acute infection, ABCs primarily reside in the spleen and differentiate into antibody-secreting cells upon rechallenge. The figure was created using BioRender.com. ABC, age-associated B cell; ASC, antibody-secreting cell.