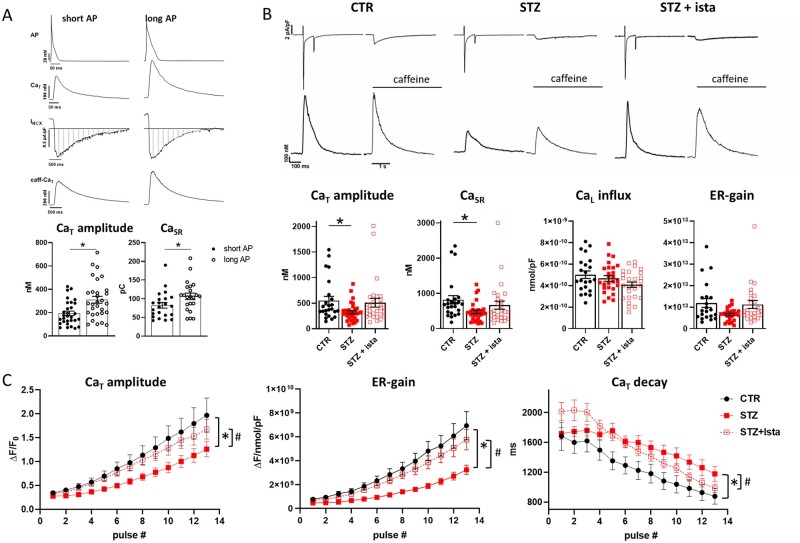
Figure 4.
STZ-induced handling changes under control of membrane potential. Analysis of istaroxime effects. (A) Top: APs waveforms (CTR and STZ APs named short and long APs, respectively) and corresponding CaT evocated in V-clamped STZ myocyte through AP-clamp experiments (2 Hz). Caffeine-induced CaT (caff-CaT) and the corresponding NCX current (INCX) were recorded at −80 mV following steady state stimulation with short and long AP to estimate changes in SR Ca2+ content (CaSR). Bottom: statistics of CaT amplitude (N = 5, n = 30) and CaSR (integral of inward INCX, marked as striped area) (N = 5, n = 22) under short and long AP stimulation. Fluorescence signals were converted to free Ca2+ estimating Fmax in each cell. *P<0.05 vs. short AP (paired t-test). (B) Top: transmembrane currents and CaT simultaneously recorded in voltage-clamped cells (Hp −35 mV) from CTR and STZ myocytes with or w/o 100 nmol/L istaroxime. Bottom: statistics of CaT amplitude, CaSR, Ca2+ influx through L-type Ca2+ channel (CaL influx), and ER gain. CTR N = 3 (n = 22–24), STZ N = 5 (w/o istaroxime n = 26–33, with istaroxime n = 28). Fluorescence signals were converted to free Ca2+ estimating Fmax in each cell. *P<0.05 vs. CTR (one-way ANOVA plus Tukey’s multiple comparison). (C) Statistics of CaT parameters (CaT amplitude, ER-gain, and CaT decay time constant) measured during each pulse after SR depletion under NCX blockade (see Supplementary material online, Figure S2) in CTR and STZ myocytes with or w/o 100 nmol/L istaroxime. *P<0.05 vs. CTR; #P<0.05 vs. STZ w/o istaroxime (two-way ANOVA); CTR N = 5 (n = 13–21), STZ N = 4 (w/o istaroxime n = 13–28, with istaroxime n = 19–24).