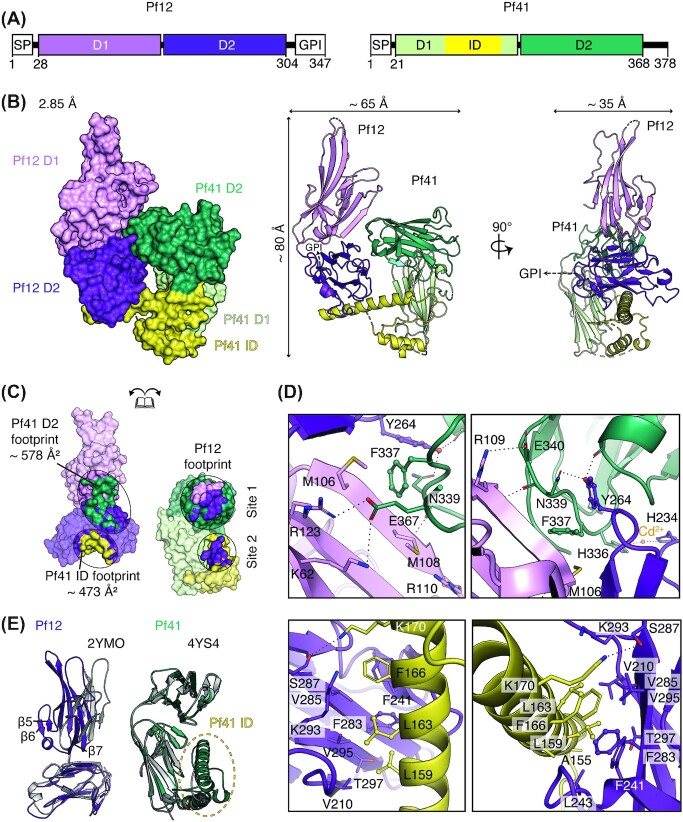
Figure 1.
Crystal structure of the heterodimeric complex of Pf12-Pf41. (A) Schematic diagram of Pf12 and Pf41 (left, right respectively). SP, signal peptide; GPI, GPI-anchor; D1, N-terminal 6-cys domain; D2, C-terminal 6-cys domain; ID, inserted-domain like region. Residue numbers are indicated. (B) Structure of the Pf12-Pf41 complex in two orthogonal views as surface representation (left) and ribbon representation (middle, right). The two 6-cys domains, D1 and D2, are shown in light and dark purple for Pf12 and in light and dark green for Pf41 respectively. Within Pf41, the inserted domain-like region (ID) which is located between the last two β-strands of D1 is coloured yellow. A dashed arrow indicates the linker region of 17 residues between the C-terminus of Pf12 D1D2 and the predicted GPI-anchor attachment site (S321) which were not included in the crystallization construct. (C) The Pf12-Pf41interface. Pf12 residues that interact with the ID of Pf41 are shown in yellow; residues that interact with the C-terminal D2 domain of Pf41 are shown in dark green. Pf41 residues that are in contact with Pf12 D1 and D2 are shown in light and dark purple, respectively. Footprints for binding sites are defined by contacting residues within 5.0 Å. (D) Interactions between the Pf12 D1-D2 interdomain region and the Pf41 D2 domain in two different orientations (top panels, left and right). Interactions between the Pf12 D2 domain and the Pf41 ID shown in two different views (bottom panels, left and right). (E) Structural overlay of Pf12 D1D2 with the published unbound Pf12 crystal structure, PDB ID 2YMO, aligned based on the D2 domain (left). Structural overlay of Pf41 D1D2 with the published unbound Pf41 crystal structure, PDB ID 4YS4 (right).