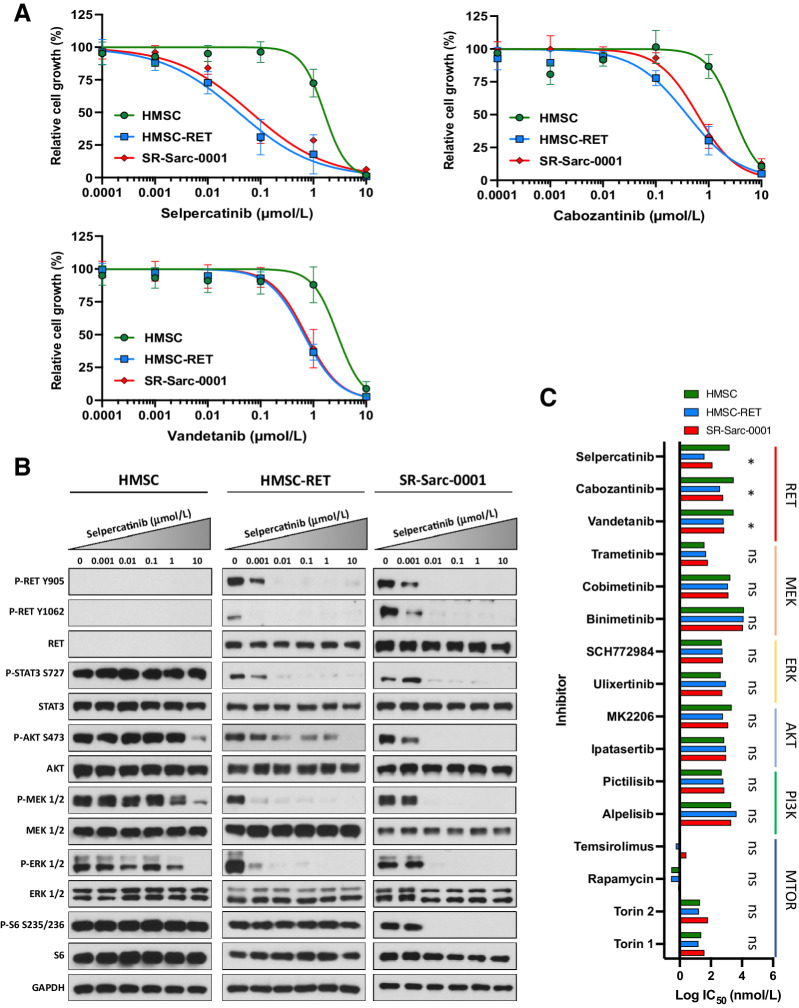
Figure 2.
SPECC1L-RET–rearranged sarcoma models are sensitive to RET inhibition. A, Sensitivity of HMSC, HMSC-RET, and SR-Sarc-0001 cells to RET inhibitors was assessed using alamarBlue cell viability assay after 96-hour treatment. Data represent the mean ± SD of 6 measurements. Resulting IC50 values and 95% CIs are shown in the bottom right panel. B, Cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of selpercatinib for 90 minutes, then whole-cell extracts were prepared for Western blot profiling. C, Sensitivity of HMSC, HMSC-RET, and SR-Sarc-0001 cells to different RET, MEK, ERK, AKT, PI3K, or mTOR inhibitors was determined. IC50 values are shown as a bar plot. IC50 values and their 95% CIs of HMSC-RET and SR-Sarc-0001 cells were compared with the parental HMSCs to determine differential sensitivity. *, P < 0.05; ns, not significant.