Figure 3. Dopamine axon signals in DMS predict punishment-resistant reward-seeking.
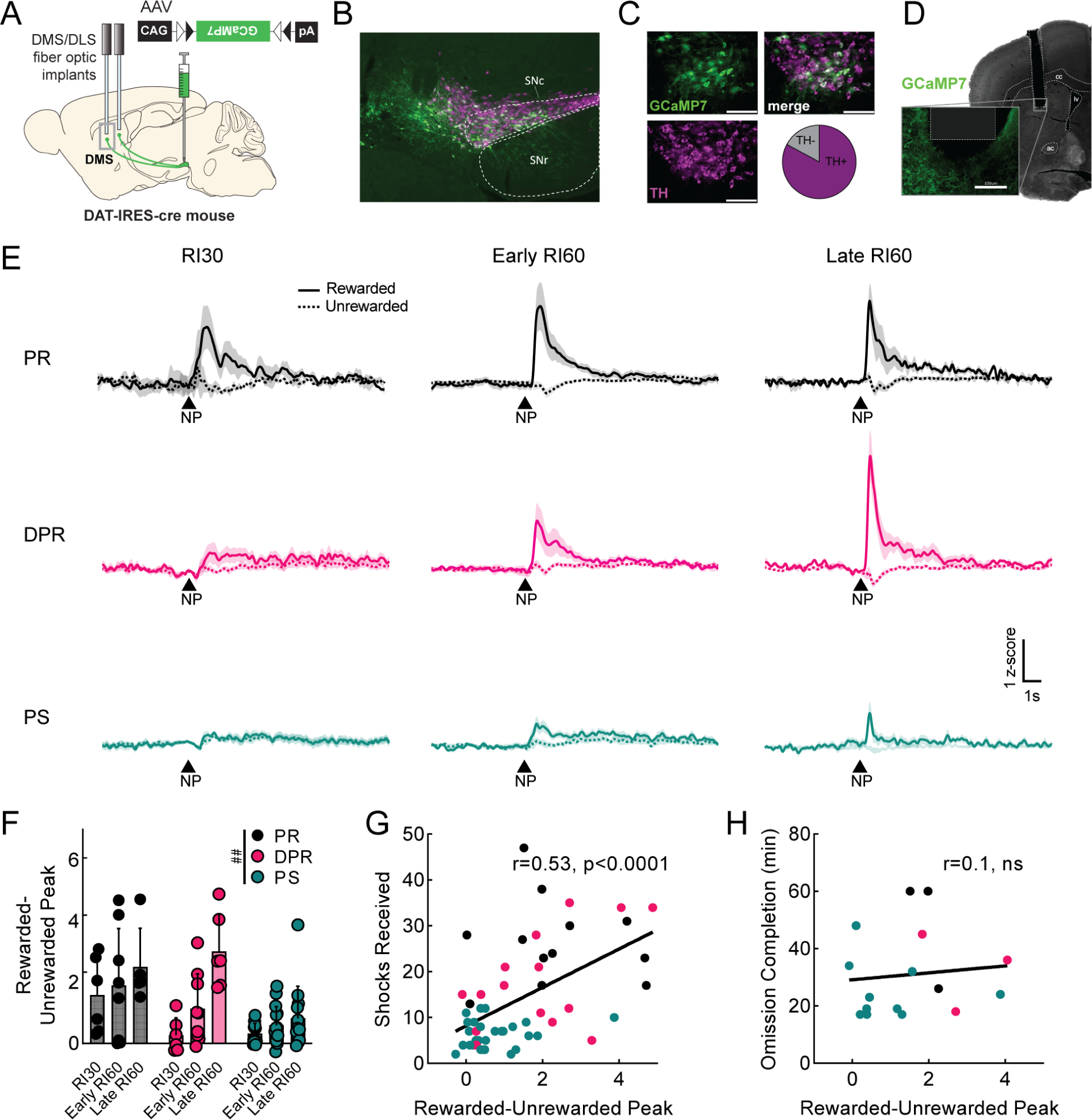
A. Viral injection and probe placement strategy. B. Representative image (4x) showing viral spread of GCaMP7b (green, all images) and TH positive cells (magenta, all images) in midbrain. Scale bar is 100μm (all images). SNc=substantia nigra pars compacta. SNr=substantia nigra pars reticulata. C. 40x images of SNc showing GCaMP7b, TH positive cells, and merged image. Quantification of GCaMP7b-expressing cells that are TH+ is shown; n=572 cells. D. Representative image showing probe placement in DMS. Area of magnification shows GCaMP7b expression in dopaminergic axons near probe. cc=corpus callosum, lv=lateral ventricle, ac=anterior commissure. E. Peri-stimulus time histograms (PSTHs) showing average signal from DMS dopamine terminals at rewarded (solid) and unrewarded (dashed) nosepokes (NP) for each phenotype during RI30 training, early, and late RI60 training. Shaded region represents SEM. Punishment resistant (PR; black, RI30 n=6, early n=7, late n=5 for all panels), delayed punishment resistant (DPR; pink, RI30 n=6, early n=9, late n=6 for all panels), or punishment sensitive (PS; teal, RI30 n=11, early n=15, late n=13 for all panels). F. Quantification of average rewarded-unrewarded peak for DMS dopamine terminal signals in response to nosepokes. Error bars represent SD, main effect ##p<0.01 G. Correlation of shocks received in shock probes and rewarded-unrewarded peaks in DMS dopamine terminals (r=0.53, p<0.0001). H. Correlation of omission completion time and rewarded-unrewarded peaks in DMS dopamine terminals (r=0.1, ns). See also Figure S3.
