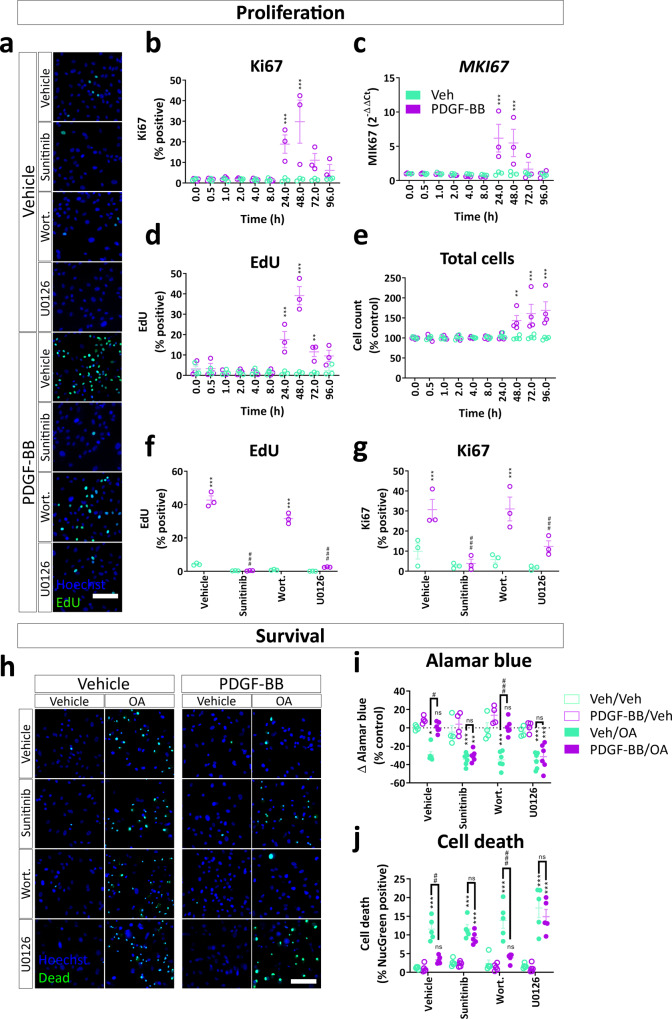
Fig. 7. PDGF-BB-dependent proliferation and protection from apoptosis are dependent on ERK signalling.
Pericytes were grown to confluence, then treated with PDGF-BB (10 ng/mL) for up to 96 h, then fixed at the endpoint and immunostained or RNA harvested for qPCR. EdU was added 24 h prior to the endpoint. Quantification of b Ki67 protein and c MKI67 gene expression following PDGF-BB stimulation. Quantification of d EdU incorporation and e cell count following PDGF-BB treatment. n = 3–4, two-way ANOVA. Pericytes were pre-treated with PDGFRβ inhibitor sunitinib (100 nM), PI3K inhibitor wortmannin (100 nM) or MEK/ERK inhibitor U0126 (10 μM) or vehicle (0.3% DMSO) for 30 min, then treated with vehicle or PDGF-BB (10 ng/mL) for 48 h. EdU was added 24 h prior to endpoint. a Representative images and quantification of f EdU incorporation and g Ki67 immunostaining in pericytes treated with PDGF-BB with or without pathway inhibitors. Pericytes were pre-treated with sunitinib (100 nM), wortmannin (100 nM) or U0126 (10 μM) or vehicle (0.3% DMSO) for 30 min, then treated with vehicle or PDGF-BB (10 ng/mL) for 24 h. n = 3, two-way ANOVA. Apoptosis inducer okadaic acid (OA; 50 nM) or vehicle was added to pericytes for a further 24 h, and viability was analysed by the AlamarBlue assay or ReadyProbes™ Cell Viability Imaging Kit. h Representative images of viability staining of pericytes treated with PDGF-BB, pathway inhibitors and OA. Scale bar = 100 μm. i Quantification of AlamarBlue fluorescence and j viability staining in pericytes. n = 6, two-way ANOVA. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs vehicle control, #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs PDGF-BB-treated.