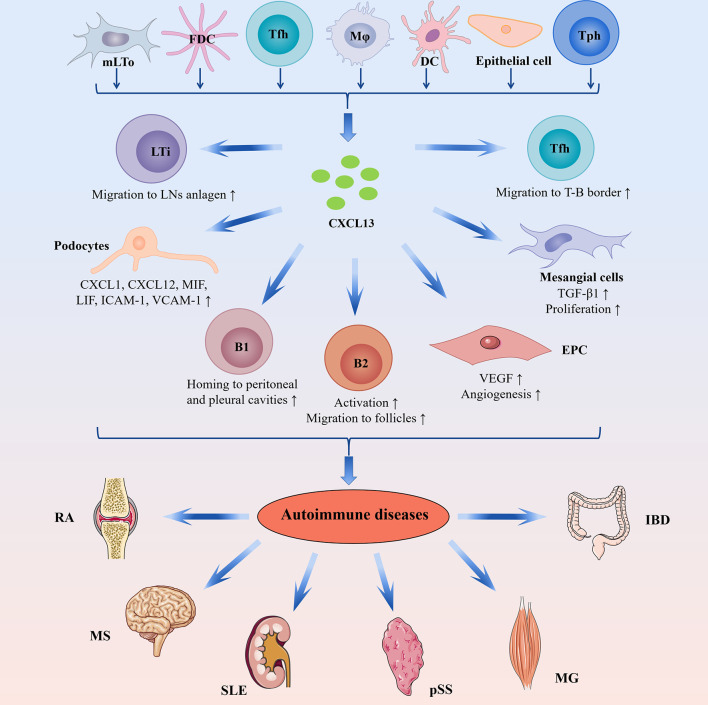
Figure 2.
The complicated role of CXCL13-mediated immune responses in autoimmune diseases. CXCL13 can be produced by mLTo cells, FDC, Tfh cells, macrophages, DCs, epithelial cells, and Tph cells. In the fetal stage, CXCL13 promotes migration of LTi cells toward the parenchyma of the LNs anlagen, where LTi cells interact with mLTo cells to induce lymphoid neogenesis. CXCL13 is involved in the lymphoid organization by attracting B cells toward B-cell follicles. During an immune response, CXCL13 attracts B cells toward the light zones of GCs, where B cells undergo affinity selection and become long-lived plasma cells or memory B cells. Furthermore, CXCL13-mediated Tfh cells migration is essential in facilitating GCs response. In addition, CXCL13/CXCR5 axis is also implicated in B1 cell response through attracting B1 cell toward the body cavity. In autoimmune diseases, ectopic CXCL13 expression promotes ectopic lymphoid neogenesis and the production of disease-specific autoantibodies. In RA, CXCL13 drives EPC homing and VEGF expression, thus inducing angiogenesis in synovial tissue. In LN, CXCL13 promotes proliferation and TGF-β1 production of mesangial cells and induces podocyte secretion of proinflammatory cytokines/chemokines such as CXCL1, CXCL12, MIF, LIF, and soluble ICAM-1 and VCAM-1. DCs, dendritic cells; EPC, endothelial progenitor cells; FDC, follicular dendritic cells; GCs, germinal centers; IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1; LN, lupus nephritis; LIF, leucocyte inhibitory factor; LTi, lymphoid tissue inducer; MG, myasthenia gravis; MIF, macrophage inhibitory factor; mLTo, mesenchymal lymphoid tissue organizer; MS, multiple sclerosis; pSS, primary Sjögren’s syndrome; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; Tfh, T follicular helper; TGF-β1, transforming growth factor β1; Tph, T peripheral helper; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.