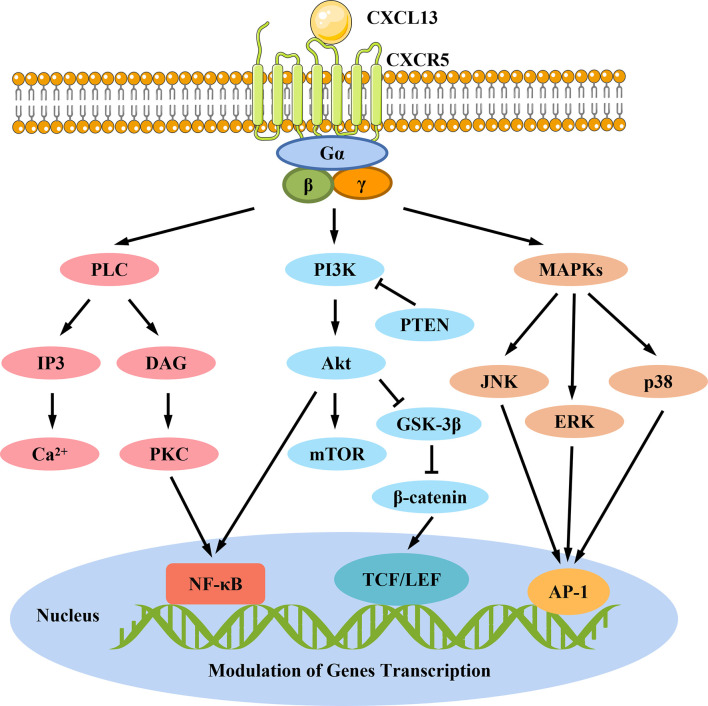
Figure 4.
CXCL13/CXCR5-mediated signaling pathways. CXCL13 exerts its biological functions through activating CXCR5, a chemokine receptor coupled to G-protein heterotrimer. Upon activation, CXCR5 undergoes conformation change and induces the cycle of G-protein activation, leading to a cascade of downstream signal transduction pathways including: (1) activation of PLC leads to conversion of PIP2 to IP3 and DAG. IP3 can promote the release of Ca2+ from intracellular stores into the cytoplasm. On the other hand, DAG consistent with increased Ca2+ activate PKC, which contributes to the activation of transcription factor NF-κB to promote cell migration; (2) activation of PI3K can trigger the activation of Akt, thus stimulating downstream NF-κB, mTOR, and GSK-3β/β-catenin/TCF/LEF signaling, which play key roles in tumor cell growth, proliferation, invasion, and migration; (3) CXCR5 also activates MAPK pathways utilizing JNK, ERK, and p38 via G-protein, which may further stimulate AP-1 to promote cell proliferation and inflammation. AP-1, activating protein-1; DAG, diacylglicerol; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; GSK-3β, glycogen synthase kinase-3β; IP3, inositol triphosphate; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PKC, protein kinase C, PLC, phospholipase C; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homologue; TCF/LEF, T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer-binding factor.