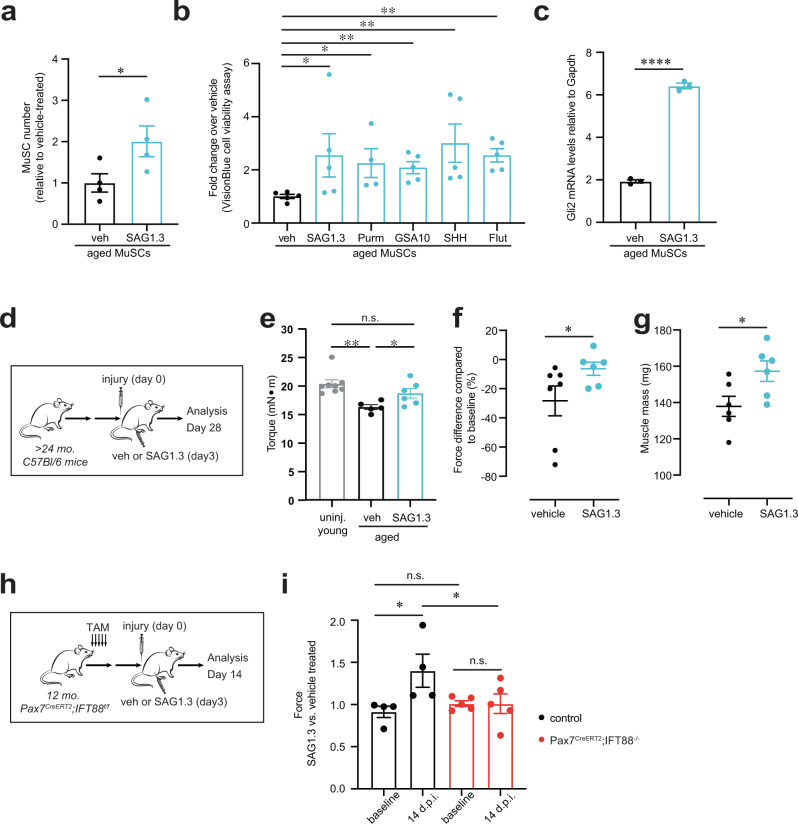
Fig. 5. SMO agonist promotes MuSC proliferation and function in aged MuSCs.
a Proliferation of aged MuSCs (>24 mo) treated with vehicle (veh) or SAG1.3 (50 nM), shown as fold change normalized to vehicle treated (n = 4 mice per condition, each with 3 technical replicates). b Proliferation of aged MuSCs treated with SMO agonist, shown as fold change normalized to vehicle treated (50 nM SAG1.3; 1 µM Purm, Purmorphamine; 0.1 µg/ml SHH, Sonic-Hedgehog; 1 µM GSA-10; 25 nM; Flut, Fluticasone) (n = 5 technical replicates per condition). c Expression levels of SMO downstream target Gli2 in MuSCs 24 h after vehicle or SAG treatment (n = 3 mice per condition). d–g Aged (>24 months) mice were injected with vehicle or SAG post-notexin injury and muscle regeneration was analyzed 4 weeks later as force recovery. d Experimental scheme. e Plantar flexion tetanic torque (absolute values) (n = 6 mice per condition). f Plantar flexion tetanic torque relative to baseline (n = 6 mice per condition). (g) Gastrocnemius muscle mass (n = 6 mice per condition). h, i) Aged control Pax7CreERT2;IFT88f/f (control, corn oil) and Pax7CreERT2;IFT88−/− (IFT88−/−, tamoxifen) mice treated with vehicle or SAG1.3 post-notexin injury and muscle regeneration was analyzed 14 days later. h Experimental scheme. i Force measurement was normalized to contralateral leg injected with vehicle. Normalized force is shown at baseline (prior to treatment) and 14 days post-injury (d.p.i) (n = 4 control and n = 5 IFT88−/− mice). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 ****P < 0.0001. Paired t test compared to vehicle treated (a, b). Mann–Whitney test (c, f, g). ANOVA test with Fisher’s LSD for multiple comparisons (e, i). Source data are provided as a Source Data file. Means + s.e.m n.s., non-significant. uninj., uninjured.