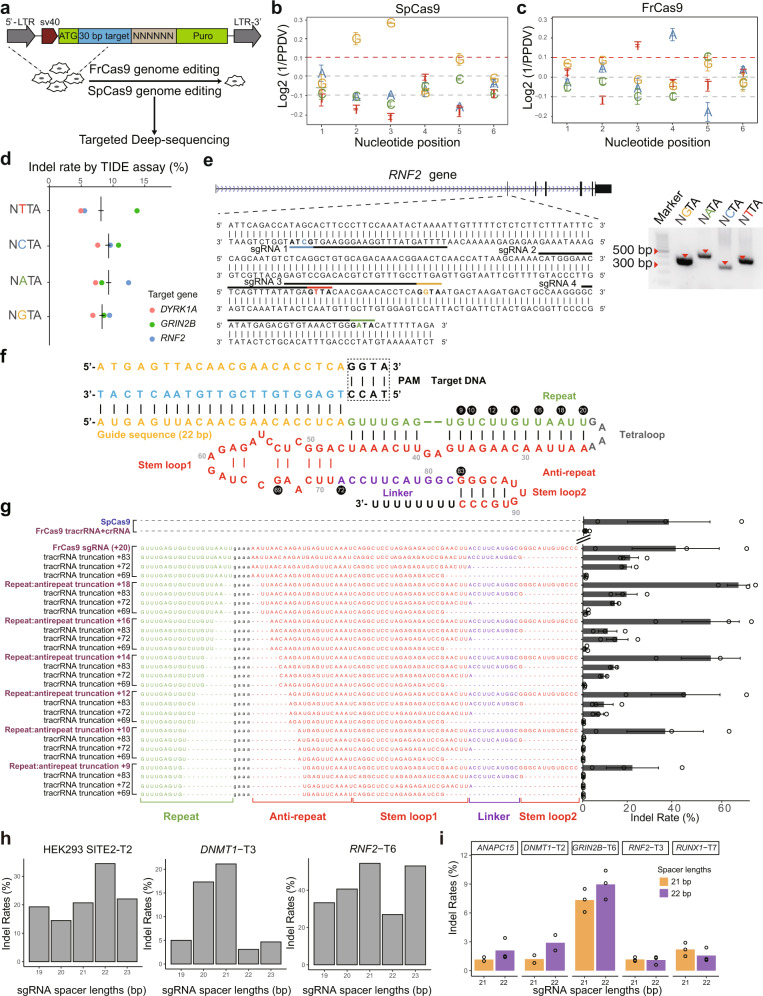
Fig. 2. FrCas9 is active in eukaryotic cells.
a The schematic of puromycin depletion assay. b, c The PAM results of SpCas9 and FrCas9 from the puromycin depletion assays. Data are presented as mean values ± S.E.M. (n = 3 biological independent replicates). d The TIDE assay showed FrCas9-induced indel rates in 3 human genes by 12 sgRNAs, which differed in the 2nd PAM base. e Genome editing by FrCas9 in the human RNF2 gene, validated by double-stranded oligodeoxynucleotide (dsODN) breakpoint PCR. And the Sanger sequencing was in Supplementary Fig. 2. Uncropped gel image is provided in Source Data. f The schematic representation of the sgRNA:target DNA complex. g The efficiency of sgRNAs with truncated scaffolds of FrCas9 assayed by target amplicon sequencing. Data are presented as mean values ± S.E.M. (n = 3 biological independent replicates). h The FrCas9 editing efficiencies with 19–23 bp spacer lengths in three human sites by target amplicon sequencing. i The FrCas9 editing efficiencies with 21 and 22 bp spacer lengths in five human sites by TIDE (n = 3 biological independent replicates). Source data are provided with this paper.