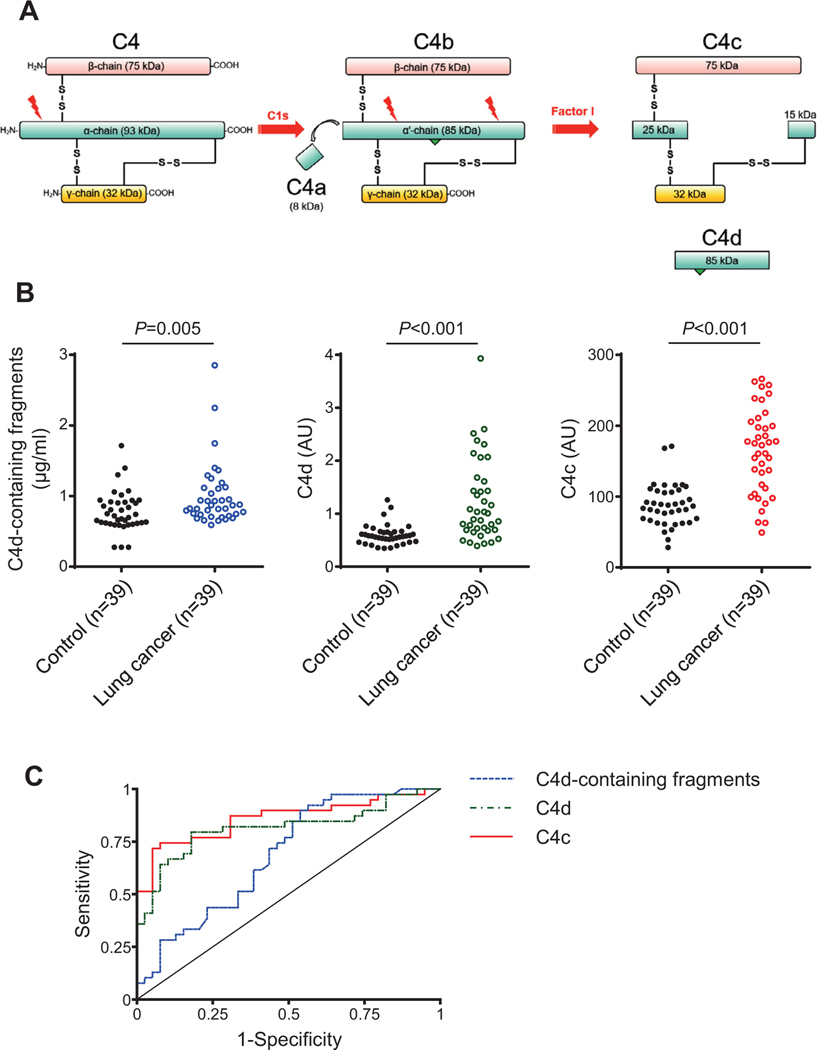
Fig 2.
Performance of C4-derived fragments as diagnostic markers for lung cancer. A) Scheme representing the proteolytic formation of C4-derived fragments upon activation of the classical pathway of complement. C4a and C4c are soluble fragments, whereas C4b and C4d remain covalently attached to the target membrane (the location of the membrane-binding site is indicated by a green triangle). C4b, C4d, and iC4d (an intermediate fragment not shown in the figure) are designated in this manuscript as C4d-containing fragments derived from C4 activation. B) Quantification of C4d-containing fragments, C4d and C4c plasma levels in patients diagnosed with early-stage NSCLC (n = 39) and matched control subjects (n = 39). The P value was calculated using the 2-sided Mann-Whitney U test. AU: Arbitrary units. C) ROC curves obtained from the plasma levels of the three markers.