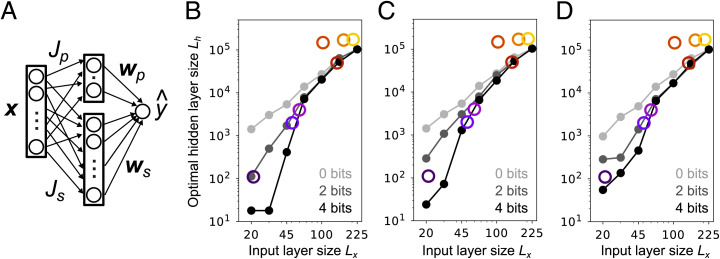
Fig. 6.
Olfactory circuit augmented with a genetically specified pathway. (A) Schematic of the two-pathway model. For the top part of the circuit, the weights and are hard wired; for the bottom part, the weights are randomly connected and are learned with adaptive SGD. (B–D) Optimal layer size of the projection neurons-to-Kenyon cells pathway under different model settings. (B) Low-bit synapses were achieved by adding Gaussian noise to and . (C) Low-bit synapses were achieved by discretizing and . (D) Low-bit synapses were achieved by adding noise to and as in B, but was additionally learned from training samples using SGD (SI Appendix, Eq. S145). In B–D, the teacher network had a hidden-layer size of 500 and a ReLU nonlinearity, and we used and trials. For sb = 2 bits we used , while for sb = 4 bits we used . For sb = 0 bits, we simply removed the hard-wired pathway. The width of the hard-wired intermediate layer, Lp, was found from Eq. 18: , rounded up to an integer. See SI Appendix, sections 6 and 7.5 for details.