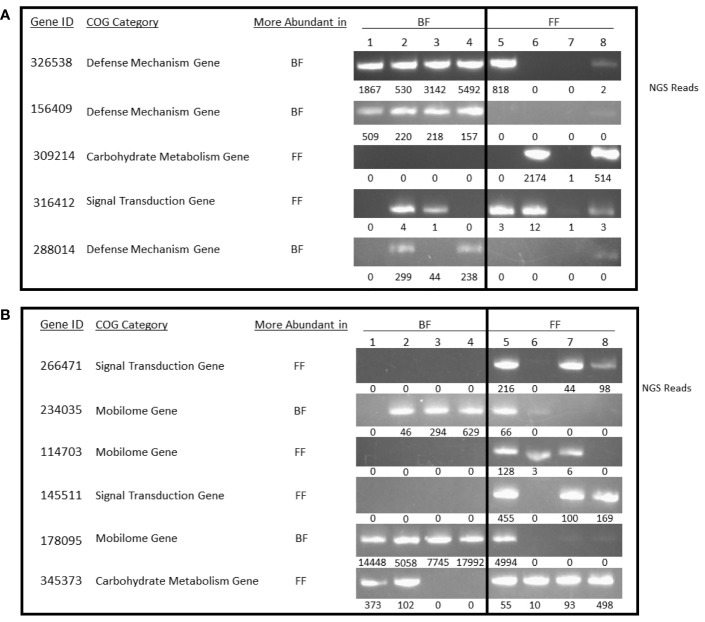
Figure 3.
Gene Amplification. (A, B) Non-quantitative PCR was used to validate the results of the bioinformatic analysis for 11 genes. Four representative samples from each cohort of breast-fed and formula-fed infants were analyzed using the purified DNA extracts. Next generation sequencing reads are shown under each PCR panel, as well as corresponding cohort with a higher abundance of the Clusters of Orthologous Genes category. (A) 326538, toxin component of the Txe-Axe toxin-antitoxin module, Txe/YoeB family; 156409, alkyl hydroperoxide reductase subunit AhpF; 309214, glycogen synthase; 316412, c-di-AMP phosphodiesterase, consists of a GGDEF-like and DHH domains; 288014, S-formylglutathione hydrolase FrmB. (B) 266471, chemotaxis protein CheY-P-specific phosphatase CheC; 234035, conjugal transfer/entry exclusion protein; 114703, phage DNA packaging protein, Nu1 subunit of terminase; 145511, adenylate cyclase, class 3; 178095, protein involved in initiation of plasmid replication; 345373, sensor histidine kinase regulating citrate/malate metabolism.