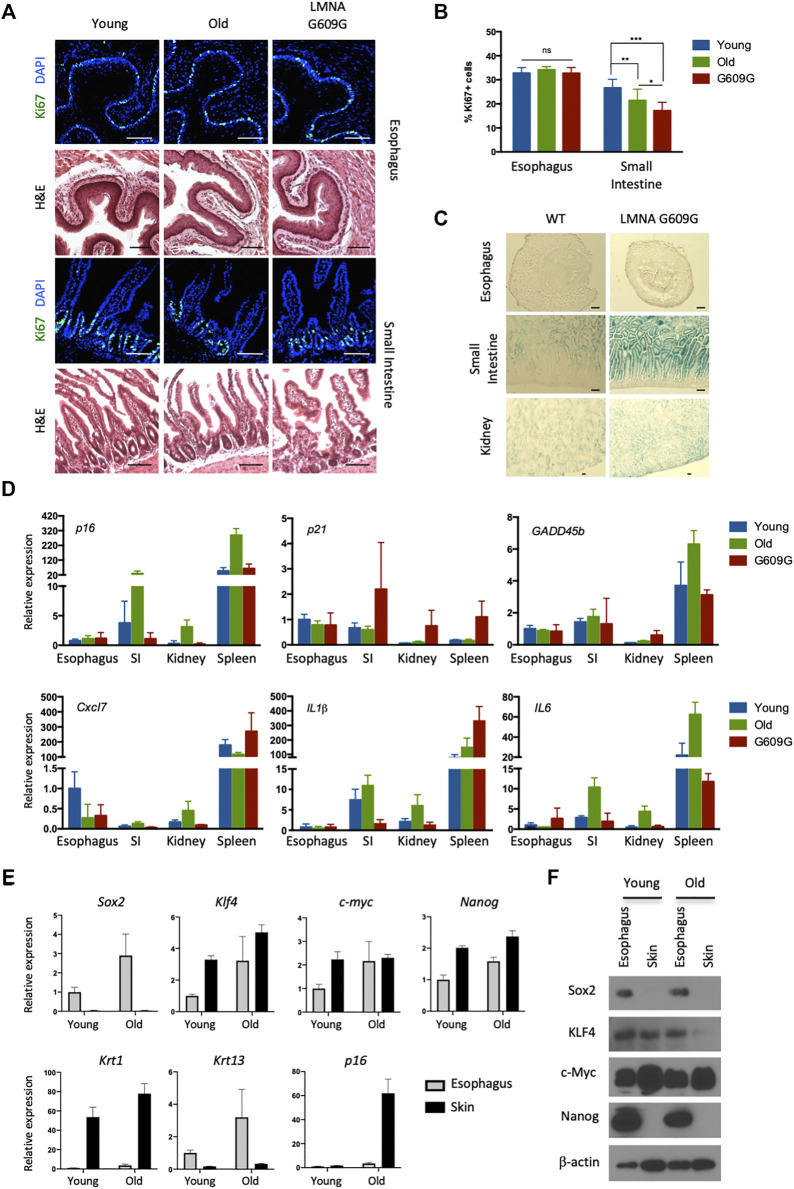
FIGURE 1.
No visible senescence of esophageal epithelial cells expressing pluripotency factors. (A) Representative immunofluorescent pictures of Ki67 (green) staining and H&E staining in the esophagus and small intestine for young (3 months old), old (22 months old) and LMNA G609G HGPS mouse model (3 months old). Scale bars, 100 μm. (B) Proliferative index of the esophagus and small intestine. We quantified Ki67+ cells in the esophagus and small intestine from three mice for each group. Data represent the mean with SD. ns = non-significant, *p < 0.01, **p < 0.001, ***p < 0.0001. (C) SA-βgal staining in the esophagus, small intestine and kidney for both young (3 months old) and LMNA G609G HGPS mouse models (3 months old). Scale bars, 100 μm. (D) qPCR analysis for aging markers. SI: Small Intestine. Data represent the mean with SE (n = 3). (E) qPCR analysis for the esophagus and the skin from young and old mice. Krt1 and krt13 were used as specific keratins for the skin and the esophagus, respectively. Data represent the mean with SE (n = 3). (F) Western blotting for pluripotency factors. Epithelial cells were isolated from the indicated tissues and cultured for 1 week before cell lysate preparation.