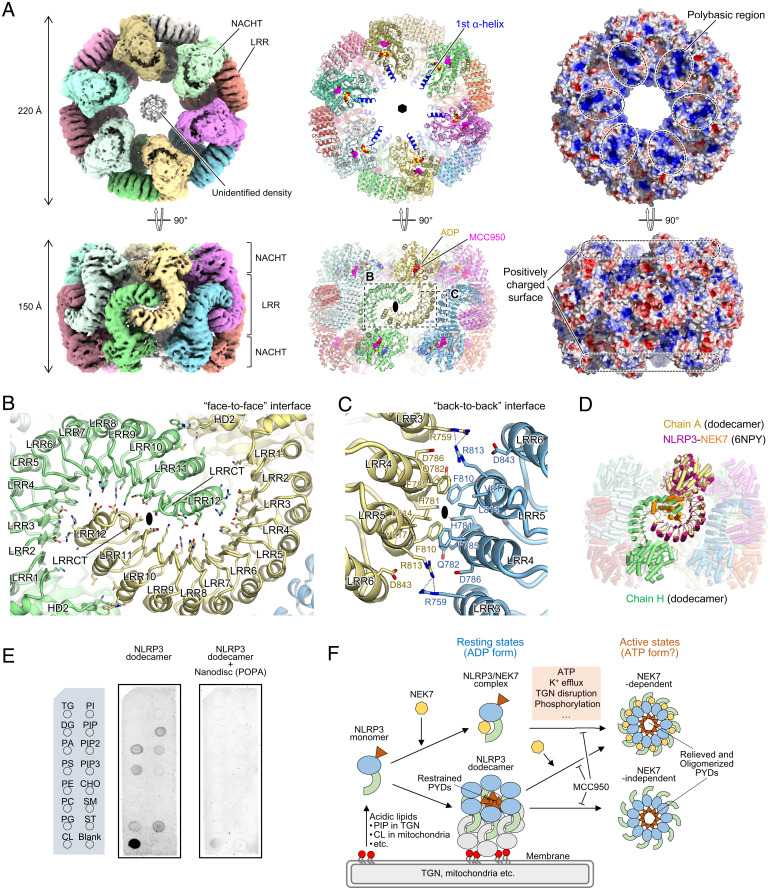
Fig. 3.
Structure of the full-length mouse NLRP3 dodecamer. (A) Overall structure of the full-length mouse NLRP3 dodecamer. Cryo-EM map (Left), ribbon model (Middle), and electrostatic surface potentials (Right) are shown. Each protomer is shown in a different color. ADP and MCC950 molecules are shown as yellow and pink spheres, respectively, in the ribbon model. Both sixfold and twofold axes are shown in the ribbon model. The first α-helix of the NACHT domain is shown in blue in the ribbon model. (B and C) Close-up views of the “face-to-face” (B) and “back-to-back” (C) interfaces. Hydrogen bonds are indicated by dashed lines. The twofold axes are shown. (D) Superposition of the NLRP3-NEK7 complex (PDB 6NPY) onto one protomer in the mouse NLRP3 dodecamer. NLRP3 and NEK7 in the NLRP3-NEK7 complex are shown in dark pink and orange, respectively. (E) Membrane lipid-binding assay of the NLRP3 dodecamer in the absence or presence of POPA-reconstituted nanodiscs (ND). Layout of the membrane lipid strip sheet (Left) and images of the lipid strip sheet detected by chemiluminescence for the NLRP3 dodecamer (Middle) and NLRP3 dodecamer with POPA-reconstituted ND (Right) are shown. TG, triglyceride; DG, diacylglycerol; PA, phosphatidic acid; PS, phosphatidylserine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PG, phosphatidylglycerol; CL, cardiolipin; PI, phosphatidylinositol; PIP, PtdIns(4)P; PIP2, PtdIns(4,5)P2; PIP3, PtdIns(3,4,5)P3; CHO, cholesterol; SM, sphingomyelin; ST, sulfatide. (F) NLRP3 inflammasome activation model. NEK7-NLRP3 binding and the resting-state oligomerization of NLRP3 (this study) are mutually exclusive events. The NLRP3 dodecamer attaches to the trans-Golgi network (TGN) or mitochondrial membranes via its polybasic region binding to acidic lipids, such as PIP and PA. The NLRP3 inhibitor, MCC950, binds to and stabilizes the closed form of NLRP3, thereby suppressing the disruption of oligomers or structural changes to the open form for NLRP3 activation. Multiple factors are individually or concertedly involved in NLRP3 inflammasome activation, some of which could regulate the activation by directly or indirectly affecting the oligomerized state of NLRP3.