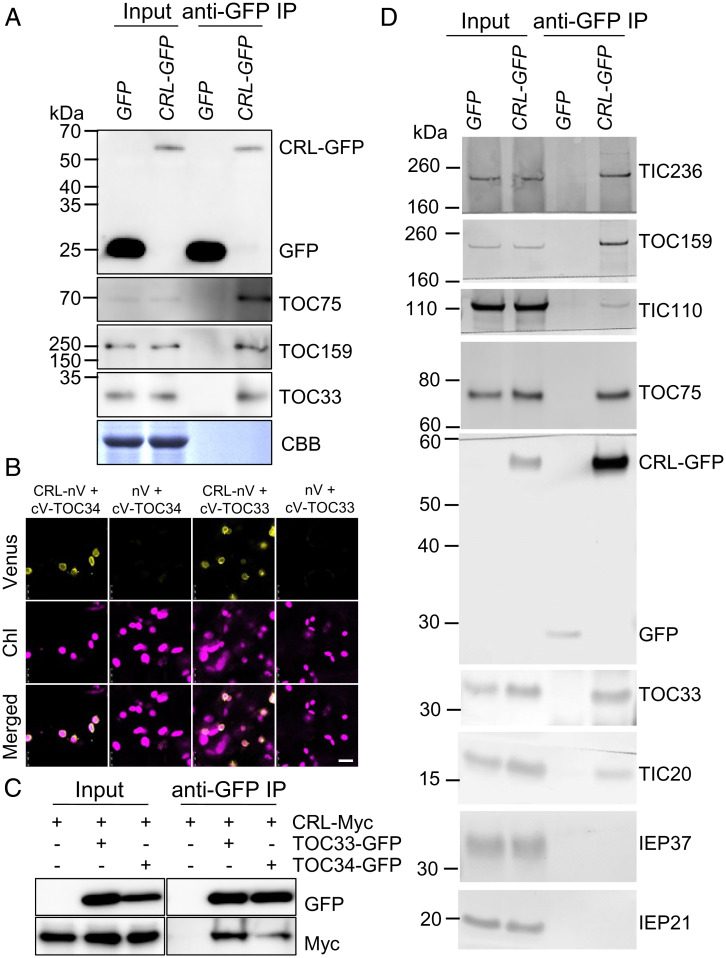
Fig. 3.
CRL is associated with translocon. (A) Co-IP/immunoblot results of CRL-TOC interactions. WT Arabidopsis expressing GFP and CRL-GFP–complemented crl transgenic plants were used. Total proteins were extracted from 5-d-old seedlings and then GFP and CRL-GFP were pulled down. Subsequent immunoblot analysis was conducted using the indicated TOC and TIC antibodies. Coomassie blue (CBB) staining of the SDS-PAGE gels is shown as a loading control (for input samples). (B) BiFC analysis. nV-fused CRL and cV-fused TOC33 (or TOC34) were transiently coexpressed in N. benthamiana leaves. The empty nV vector was used as a negative control. The representative Venus signals, chlorophyll autofluorescence (Chl) signals, and their merged images are shown. (Scale bar, 10 μm.) (C) Co-IP/immunoblot analysis. Different construct combinations, such as CRL-Myc alone, CRL-Myc and TOC33-GFP, or CRL-Myc and TOC34-GFP, were transiently overexpressed in N. benthamiana leaves. After 2 d, GFP-Trap magnetic beads were used to enrich the target and its associated proteins. Subsequent immunoblot analyses were carried out by using anti-GFP and anti-Myc antibodies. (D) Chloroplasts were isolated from WT Arabidopsis expressing GFP and CRL-GFP–complemented crl transgenic plants and hypotonically lysed. Total membranes were solubilized with 1% decylmaltoside and immunoprecipitated with GFP-Trap magnetic particles (Chromotek). Immunoprecipitates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblots with antibodies indicated on the right.