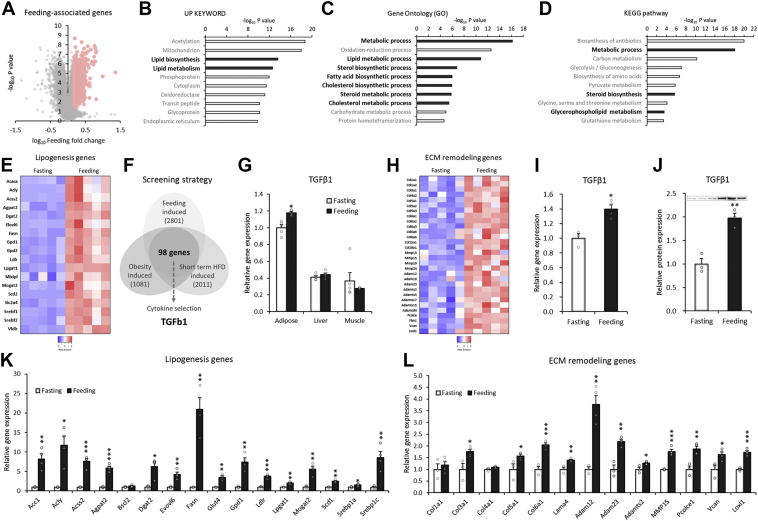
Figure 1.
The feeding-related lipogenic pathway is associated with TGF-β1 and the related ECM remodeling factors in adipose tissue.A–E, transcriptome analysis in adipose tissue of 24 h fasted C57BL/6J mice and chow-fed controls (GSE46495). Feeding-associated genes in mouse adipose tissues were selected (A) and analyzed with the Up Keyword (B), Gene Ontology (C), and KEGG pathway databases (D). E, heatmap of lipogenesis-related genes in mouse adipose tissues from 24 h fasting and ad libitum feeding states (GSE46495, n = 5). F, schematic diagram of microarray analysis to identify feeding-induced factors expressed in adipose tissue and adipocytes. The following Gene Expression Omnibus datasets were used for the analysis: feeding-induced genes in mouse adipose tissue (GSE46495, fold change >1.17, p < 0.05; 2801 genes), short-term high-fat diet–induced genes in mouse adipose tissue (GDS5824, fold change >1.25, p < 0.05; 2011 genes), and obesity-induced genes in human adipose tissue (GDS3602, fold change >1.25, p < 0.05; 1081 genes). G, relative expression of the TGF-β1 gene in mouse adipose tissues, liver, and skeletal muscle from 24 h fasting and ad libitum feeding states (GSE46495, n = 5). H, heatmap of ECM remodeling–related genes in mouse adipose tissues from 24 h fasting and ad libitum feeding states (GSE46495, n = 5). I, relative TGF-β1 RNA and protein expression of gonadal WAT from C57BL/6J mice fasted for 48 h and mice refed for 48 h (n = 3). J, relative TGF-β1 protein levels in gonadal WAT of C57BL/6J mice fasted for 24 h or refed for 12 h (n = 3). K and L, relative expression of the indicated genes in gonadal WAT from 48 h fasted or refed mice (n = 3). Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. ECM, extracellular matrix; KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; TGF-β1, transforming growth factor β1; WAT, white adipose tissue.