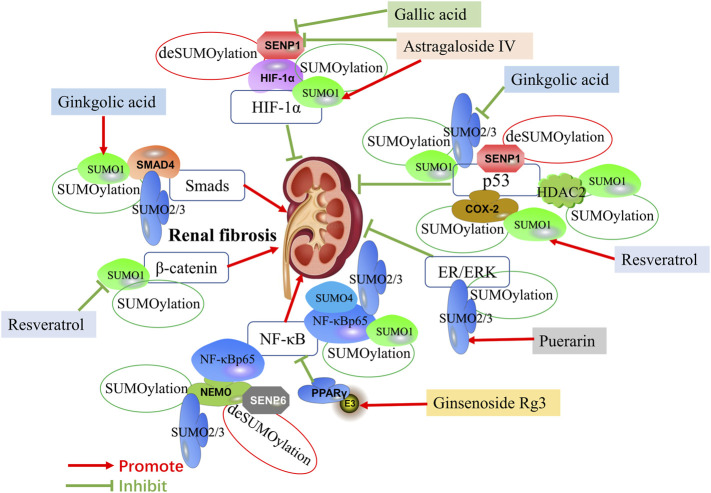
FIGURE 1.
Mechanisms of SUMOylation and deSUMOylation by transcription factors in renal fibrosis and therapeutic targets of natural products against renal fibrosis via SUMOylation. Mechanisms of SUMOylation and deSUMOylation by transcription factors in renal fibrosis are including TGF-β/Smad signaling, HIF-1α signaling, p53 pathway, ER/ERK pathway, NF-κB signaling, and β-catenin pathway. Smad4 is SUMOylated by SUMO1 and SUMO2/3. HIF-1α is SUMOylated by SUMO1. P53 is SUMOylated by SUMO1 and SUMO2/3, and also is upregulate by HDAC2 and COX-2 SUMOylated by SUMO1. ER/ERK is SUMOylated by SUMO2/3. NF-κBp65 is SUMOylated by SUMO1, SUMO2/3 and SUMO4, and also is upregulate by NEMO SUMOylated by SUMO2/3. PPARγ activated by SUMO ligase E3 could inhibit NF-κB signaling. β-catenin is SUMOylated by SUMO1. SNEP1 deSUMOylates HIF-1α and p53. Additionally, SNEP6 deSUMOylates NEMO. Ginkgolic acid promotes the expression of Smad4 by upregulating SUMO1, while inhibits the expression of p53 by downregulating SUMO2/3. Astragaloside IV promotes the expression of HIF-1α by upregulating SUMO1 and downregulating SENP1. Gallic acid also promotes the expression of HIF-1α by downregulating SENP1. Resveratrol induces SUMOylated COX-2 by SUMO1, thus enhancing the expression of p53. In addition, Resveratrol inhibits the expression of β-catenin by downregulating SUMO1. Puerarin activates ER/ERK pathway by upregulating SUMO2/3. Ginsenoside Rg3 inhibits NF-κB by upregulating PPARγ via activating E3.