Figure 7.
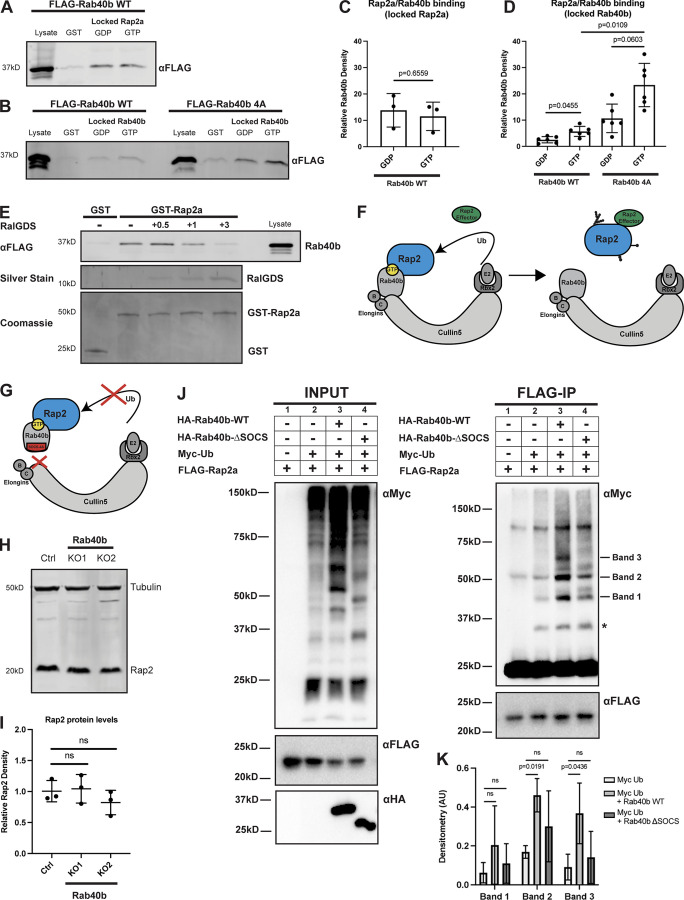
Rap2 is a Rab40b-binding protein and is ubiquitylated by the Rab40b/Cul5 complex. (A) Rab40b binding to locked Rap2a. MDA-MB-231 lysates stably expressing FLAG-Rab40b WT were incubated with either GST or GST-Rap2a, followed by a GST pull-down assay. Before incubation, GST-Rap2a was loaded with either GDP or GMP-PNP (labeled as GTP for brevity). 25 µg of lysate input was loaded as a positive control and used to estimate pull-down efficiency. (B) Rap2a binding to locked Rab40b. MDA-MB-231 lysates stably expressing FLAG-Rab40b WT or SOCS-4A (left and right, respectively) were incubated with either GST or GST-Rap2a, followed by a GST pull-down. Before incubation, FLAG-Rab40b lysates were loaded with either GDP or GMP-PNP (labeled as GTP for brevity). 25 µg of lysate input was loaded as a positive control and used to estimate pull-down efficiency. (C) Quantification of GST pull-down in A. Three biological replicates were performed. Mean ± SD. GST signal was subtracted from GDP/GTP, and relative Rab40b density was calculated by normalizing to lysate. Unpaired t test. Rab40b WT GDP versus GTP (locked Rap2a), P = 0.6559. GTP = GMP-PNP. (D) Quantification of GST pull-down in B. Six biological replicates were performed. Mean ± SD. GST signal was subtracted from GDP/GTP, and relative Rab40b density was calculated by normalizing to lysate. Brown–Forsythe ANOVA with Dunnett’s T3 multiple comparisons test. Rab40b WT GDP versus GTP (locked Rab40b), P = 0.0455; Rab40b SOCS-4A GDP versus GTP (locked Rab40b), P = 0.0603; Rab40b WT GTP versus Rab40b SOCS-4A GTP (locked Rab40b), P = 0.0109. GTP = GMP-PNP. (E) Competitive binding experiment between FLAG-Rab40b, GST-Rap2a, and untagged RalGDS (RBD). MDA-MB-231 lysates stably expressing FLAG-Rab40b WT (GMP-PNP loaded) were incubated with either GST or GST-Rap2a (GMP-PNP loaded) and increasing concentrations of RalGDS (0.5, 1, and 3 times the amount of GST/GST-Rap2a). 15 µg of lysate input was loaded as a positive control and used to estimate pull-down efficiency. (F) Model summarizing findings in A–D. Rap2 preferentially binds Rab40b-GTP (left). Ubiquitylation of Rap2 by Rab40b/Cul5 and subsequent complex dissociation is necessary for Rap2 to interact with its downstream effector (in a GTP-dependent manner). (G) When the Rab40b/Cul5 complex is disrupted (SOCS-4A mutant), Rab40b binds more strongly to Rap2. We propose that this is due to lack of ubiquitylation/complex dissociation. (H) Rap2 protein levels Ctrl versus Rab40b KO cells. Ctrl and Rab40b KO MDA-MB-231 lysates were probed for αRap2 and αTubulin (loading control). Ctrl cells are dox-inducible Cas9 MDA-MB-231s that were used to generate CRISPR lines. 50 µg of lysate was loaded for each sample. (I) Quantification of Western blot in H. Three biological replicates were performed. Relative intensity of Rap2 was normalized to the levels of Tubulin and to Ctrl cells. Mean ± SD. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. (J) Rap2a ubiquitylation in HEK293T cells. HEK293Ts were transfected with pRK5-FLAG-Rap2a ± pRK5-Myc-Ub, pRK7-HA-Rab40b, or pRK7-HA-Rab40b ΔSOCS. After 24 h of transfection, cells were harvested, lysed, and immunoprecipitated with αFLAG. Left column shows lysates (input) probed for Myc, FLAG, and HA. Right column shows FLAG immunoprecipitates probed for Myc and FLAG. Tick marks on the right blot indicate the Rap2-ubiquitin bands that are increased in response to Rab40b addition. Asterisk indicates presumed mono-ubiquitylated form of Rap2 that is not stimulated by Rab40b addition. (K) Quantification of HEK293T ubiquitylation assay in J. Raw densitometry was measured for bands 1, 2, and 3 across four independent experiments. These values (arbitrary units) were then normalized to FLAG-Rap2a input levels and graphed for conditions 2 (Myc-Ub), 3 (Myc-Ub + Rab40b WT), and 4 (Myc-Ub + Rab40b ΔSOCS). Four biological replicates were performed. Mean ± SD. Two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Band 1: Myc-Ub versus Myc-Ub + Rab40b WT, ns; Myc-Ub versus Myc-Ub + Rab40b ΔSOCS, ns; band 2: Myc-Ub versus Myc-Ub + Rab40b WT, P = 0.0191; Myc-Ub versus Myc-Ub + Rab40b ΔSOCS, ns; band 3: Myc-Ub versus Myc-Ub + Rab40b WT, P = 0.0436; Myc-Ub versus Myc-Ub + Rab40b ΔSOCS, ns. Source data are available for this figure: SourceData F7.