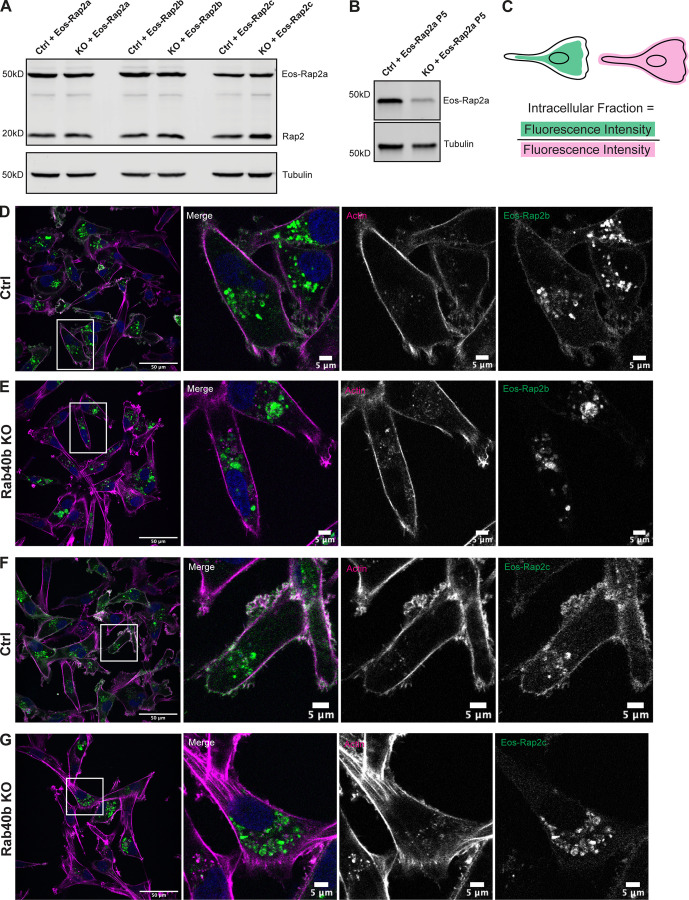
Figure S2.
Loss of Rab40b also affects Rap2b and Rap2c subcellular localization. (A) Western blot showing stable overexpression of Eos-Rap2a, Eos-Rap2b, and Eos-Rap2c in MDA-MB-231 Ctrl and Rab40b KO cells (lentivirus). Ctrl cells are MDA-MB-231 parentals. 50 µg of lysate was loaded for each sample. (B) Western blot showing stable overexpression of Eos-Rap2a in MDA-MB-231 Ctrl and Rab40b KO cells at passage 5 (lentivirus). Ctrl cells are MDA-MB-231 parentals. 50 µg of lysate was loaded for each sample. (C) Cartoon representation of intracellular/whole-cell fraction calculation (see Materials and methods). (D) Eos-Rap2b localization in MDA-MB-231 Ctrl cells. MDA-MB-231 cells stably expressing Eos-Rap2b were fixed and stained with phalloidin (magenta) and DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 50 and 5 µm. (E) Eos-Rap2b localization in Rab40b KO MDA-MB-231 cells. Rab40b KO cells stably expressing Eos-Rap2b were fixed and stained with phalloidin (magenta) and DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 50 and 5 µm. (F) Eos-Rap2c localization in MDA-MB-231 Ctrl cells. MDA-MB-231 cells stably expressing Eos-Rap2c were fixed and stained with phalloidin (magenta) and DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 50 and 5 µm. (G) Eos-Rap2c localization in Rab40b KO MDA-MB-231 cells. Rab40b KO cells stably expressing Eos-Rap2c were fixed and stained with phalloidin (magenta) and DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 50 and 5 µm. Source data are available for this figure: SourceData FS2.