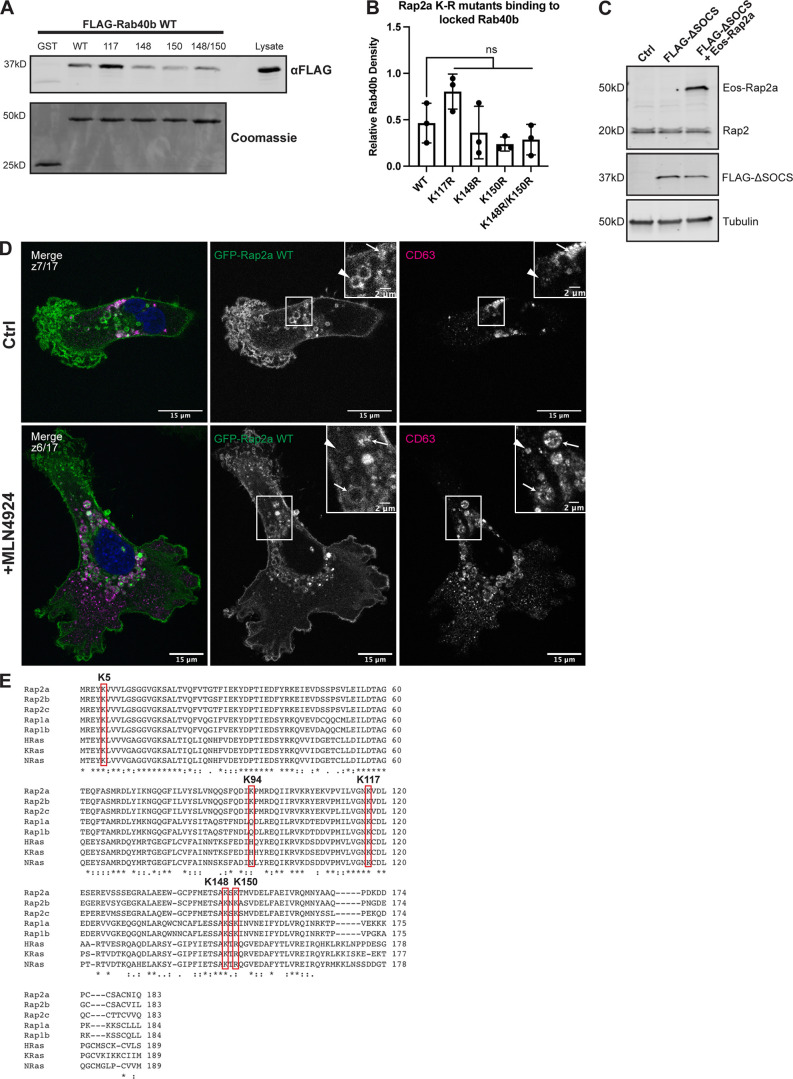
Figure S4.
Characterization of Rap2 lysine mutants and the role of Cul5 in mediating Rap2 plasma membrane targeting. (A) Rap2a K-R single/double mutants binding to Rab40b. MDA-MB-231 lysates stably expressing FLAG-Rab40b WT were incubated with GST, GST-Rap2a-WT or -K117R, K148R, K150R, or K148R/K150R, followed by a GST pull-down. Before incubation, FLAG-Rab40b lysates were loaded with GMP-PNP. GST alone was used to control for GST binding to Rab40b. 15 µg of lysate input was loaded as a positive control and used to estimate pull-down efficiency. (B) Quantification of GST pull-down in A. Three biological replicates were performed. Mean ± SD. GST signal was subtracted from experimental lanes, and relative Rab40b density was calculated by normalizing to lysate. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. ns between WT and all individual mutants. (C) Western blot showing generation of cell line in Fig. 8, L and M. Rab40b KO cells were first stably transfected with FLAG-Rab40b ΔSOCS (lentivirus, second column). The cells were then transfected with Eos-Rap2a and flow sorted (lentivirus, third column, flow sort instead of selection). Ctrl cells are dox-inducible Cas9 MDA-MB-231s that were used to generate Rab40b KO CRISPR line. 50 µg of lysate was loaded for each sample. (D) Representative images from MLN4924 experiment in Fig. 8 N. MDA-MB-231 cells stably expressing GFP-Rap2a were treated with either DMSO (Ctrl) or 300 nM MLN4924 for 24 h. Cells were then fixed and stained for CD63 (magenta) and DAPI (blue). Arrows indicate examples of GFP-Rap2a and CD63 overlap. Arrowheads point to GFP-Rap2a organelles that are not CD63 positive. Scale bars, 15 and 2 µm. (E) Protein sequence alignment of Rap2a, Rap2b, Rap2c, Rap1a, Rap1b, HRas, KRas, and NRas. Red boxes denote the five lysines within Rap2a-K5R. Stars indicate fully conserved residues. Alignment made using Clustal Omega. Source data are available for this figure: SourceData FS4.