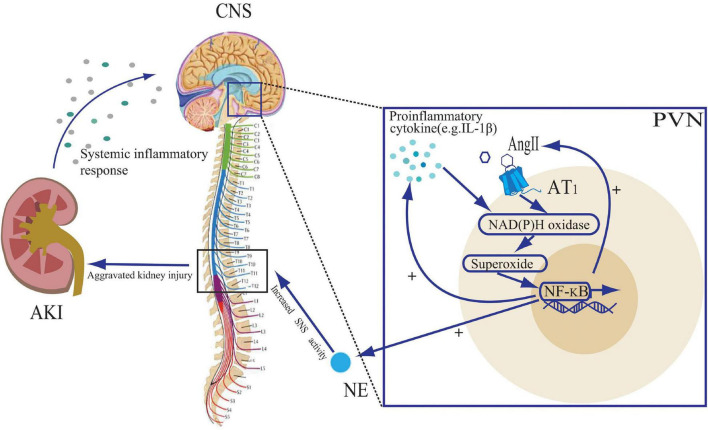
FIGURE 2.
The role of proinflammatory cytokines and angiotensin II (Ang II) in the paraventricular nuclear (PVN) during acute kidney injury (AKI). The systemic inflammatory response to AKI leads to an increase in central nervous system (CNS) pro-inflammatory cytokines. Both Ang II and pro-inflammatory cytokines stimulate NAD(P)H oxidase activity and activate the NF-κB signaling pathway, leading to further cytokine synthesis and Ang II binding to the Ang II type 1 (AT1) receptor, creating positive feedback loops. The activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway also leads to an increase in norepinephrine (NE) release, promoting sympathetic nervous system (SNS) activity, further exacerbating kidney injury.