Fig. 1 |. Dysbiosis and gut permeability contribute to lupus disease.
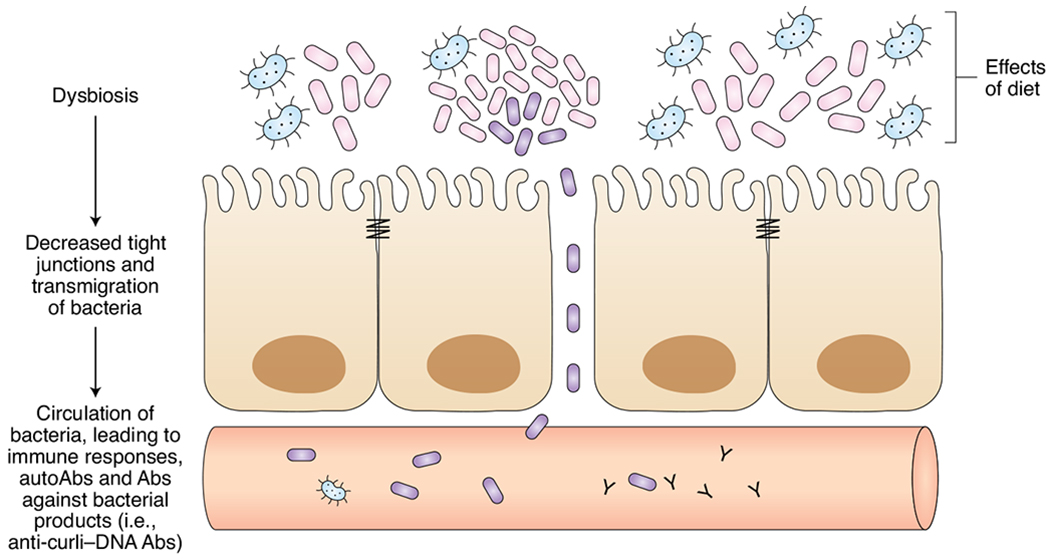
Expansion of pathogenic gut microbiota can lead to increased permeability of the gut epithelial barrier, providing a route through which bacteria and bacterial antigens can enter systemic circulation. The immune response to these foreign epitopes may generate self-reactive antibodies, such as anti-curli–DNA, and contribute to lupus pathology.
