Fig. 5, Movies 6,7. Deletion of RDEL and RDEL→RNGL mutation release HSP47 from the ER to cis-Golgi, causing Golgi disruption.
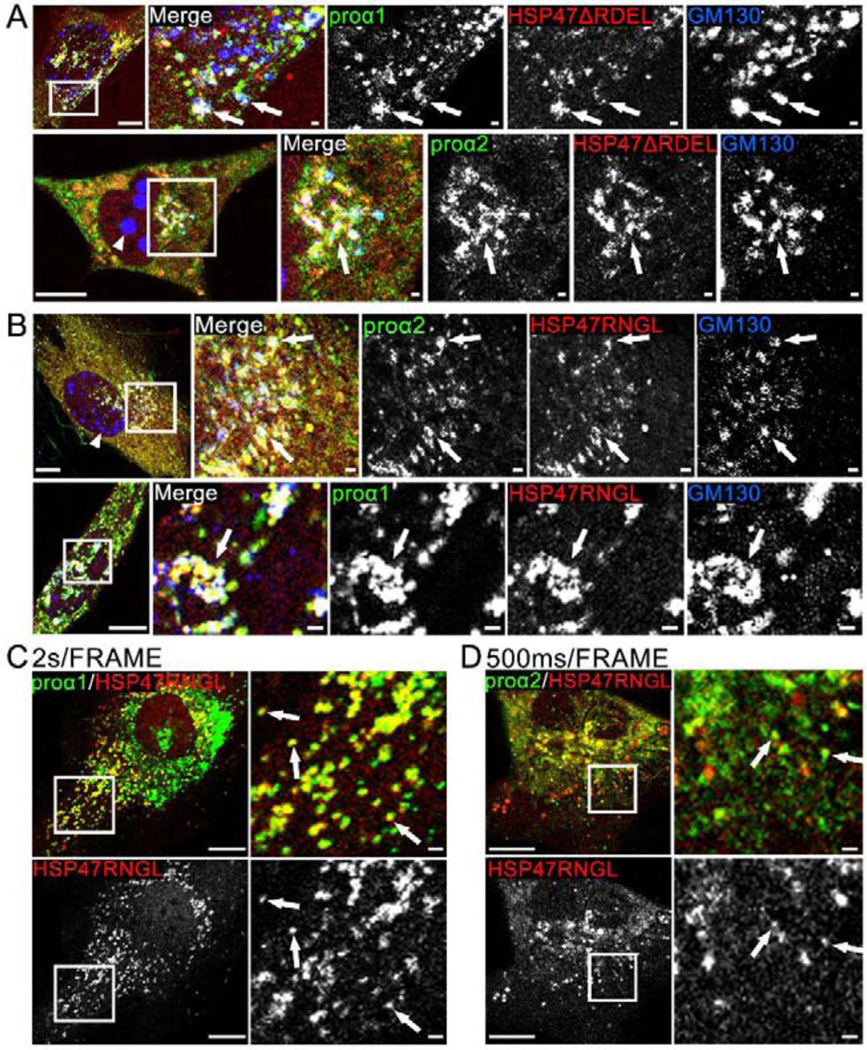
(A) Airyscan colocalization of Cherry-HSP47ΔRDEL with Venus-proα1(I)/α2(I) and cis-Golgi marker CFP-GM130 (white arrows); N=4 (proα1(I)) and N=4 (proα2(I)). Based on imaging of several z-slices, large CFP-GM130 spheres (arrowhead) are located inside the nuclei. At least some Golgi fragmentation was noticeable in all cells transfected with Cherry-HSP47ΔRDEL. (B) Airyscan colocalization of Cherry-HSP47RNGL with Venus-proα1(I)/α2(I) and cis-Golgi marker CFP-GM130 (white arrows); N=19 (proα1(I)) and N=7 (proα2(I)). In these cells, Golgi fragmentation was less pronounced. The nuclear CFP-GM130 spheres (arrowhead) were smaller and absent from some of the cells. (C, Movie 6) Confocal single slice frame and time-lapse video of Apple-HSP47RNGL colocalization with GFP-proα1(I)in transport vesicles marked by arrows in the still frame; N=63 (14 experiments). (D, Movie 7) Airyscan single slice frame and video of similar colocalization of Cherry-HSP47RNGL with Venus-proα2(I); N=18 (3 experiments). Scale bars = 10 μm (whole cell) and = 1 μm (zoom).
