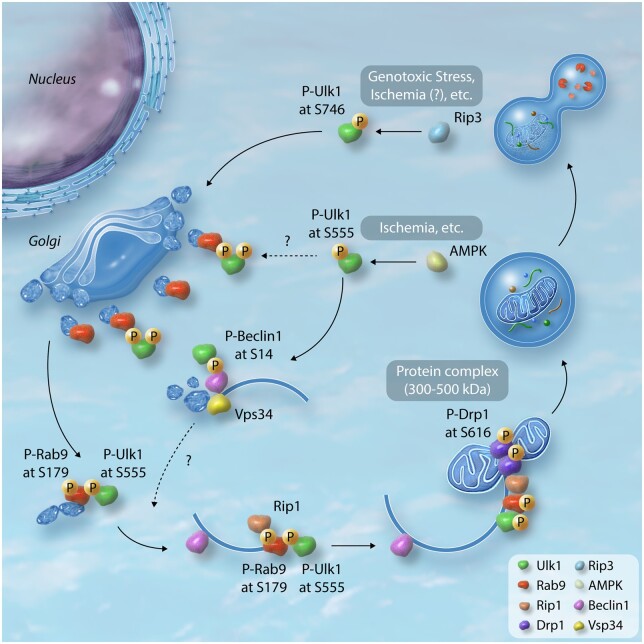
Figure 1.
Proposed model of mitophagy mediated by Ulk1-dependent alternative autophagy. Ulk1 forms protein complex with Fip200 and Atg13 at the basal state. Upon stimuli, phosphorylation of Ulk1 at serine 746 by Rip3 allows for its dissociation from the complex and translocation to Golgi.40 This mechanism was found in the MEFs under the genotoxic stress, however, its significance in the heart has yet to be clarified. The trans-Golgi network is proposed to be the origin of alternative autophagosomes. Upon energetic stress, such as ischaemia, multiple sites in Ulk1 are phosphorylated by AMPK. Of these, phosphorylation of serine 555 is important for its translocation to mitochondria in MEFs and skeletal muscle in mice.59,60 Ulk1 phosphorylates Beclin 1 at serine 14, thereby inducing the Beclin 1-Vps34 complex. Vps34 is then activated at phagophore or endosomal membranes, which is pivotal for membrane remodelling, endosomal transport and autophagy.39 Serine 555 phosphorylated Ulk1 acts as a scaffold to assemble a complex comprising Rab9, associated with trans-Golgi membranes. Ulk1 directly phosphorylates Rab9 at serine 179, that facilitates interaction between Rab9 and Rip1 and the consequent phosphorylation of Drp1 at serine 616 in cardiomyocytes.57 Mitochondria labelled with phosphorylated Drp1 are subsequently sequestrated by phagophores assembled via Rab9 in cardiomyocytes.