Figure 5.
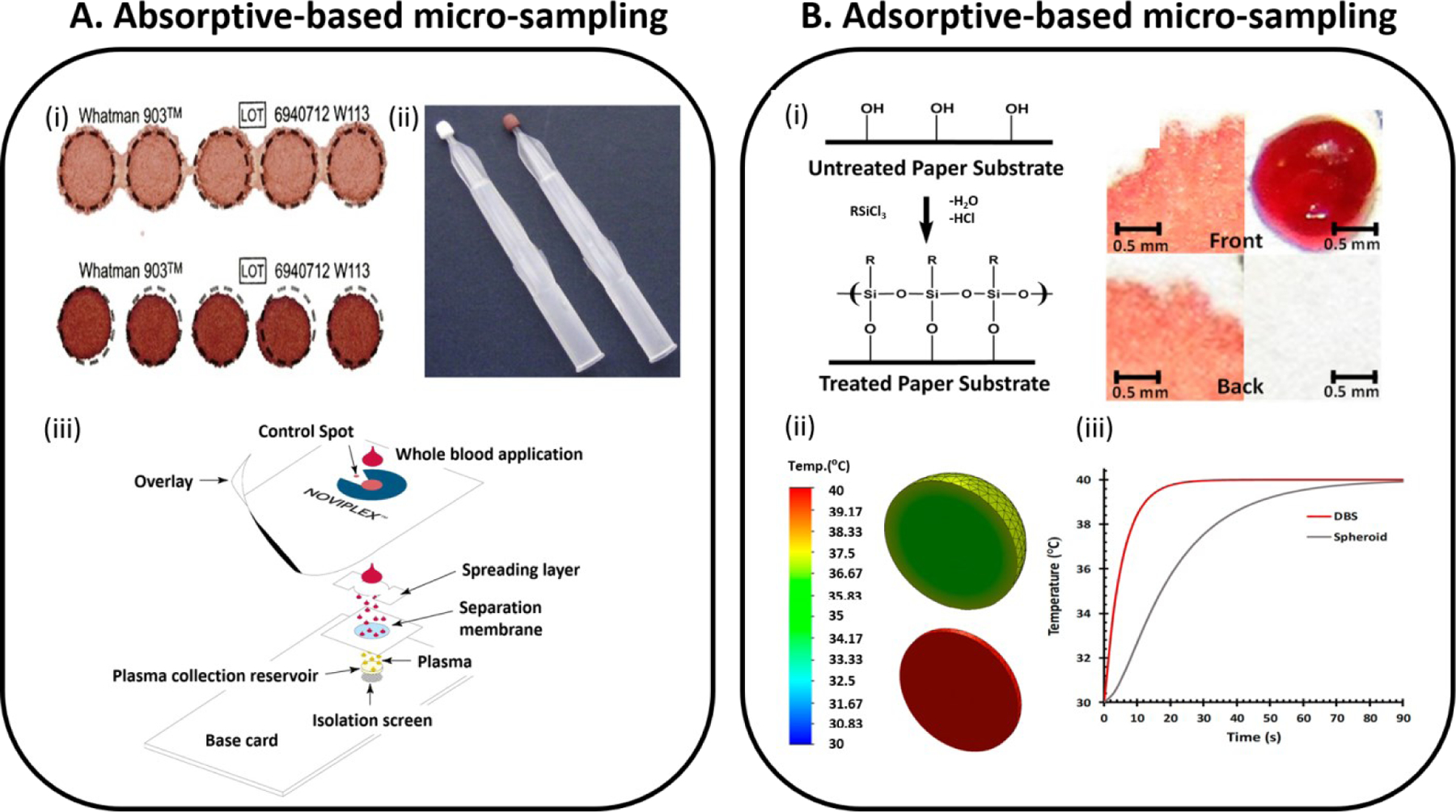
Dry-state microsampling techniques are described for the (A) traditional absorptive-based and (B) a new adsorptive-based method. (Ai) Dried blood spots at different levels of blood hematocrit (above: 0.35 and bottom: 0.50 of blood hematocrit levels respectively). Figure adopted from Reference 80 (CC BY-NC). (Aii) Volumetric absorptive microsampling (VAMS) device which enables the collection of accurate volumes (10 µL) of blood by absorption via a hydrophilic polymeric tip. Adopted with permission from Reference 81. (Aiii) Plasma extraction card is developed for rapid extracting plasma out of finger-stick blood. Alternative paper-based micro-sampling technology is developed based on adsorption phenomenon that occurs because of differences between surface tension of biofluids and surface energies of treated paper substrates. Adopted with permission from Reference 84. Hydrophobic paper substrates are prepared via a gas-phase silanization process (Bi), allowing three-dimensional (3D) spheroids of dried biofluids to be formed when a drop of biofluid is deposited and fully dried (Bii). Transient thermal analysis was simulated for a comparison between the 2D dried blood spots and the 3D blood spheroids (Biii). Panel (Bi) adapted with permission from Reference 56 and panel (Bii and Biii) adopted with permission from Reference 92.
