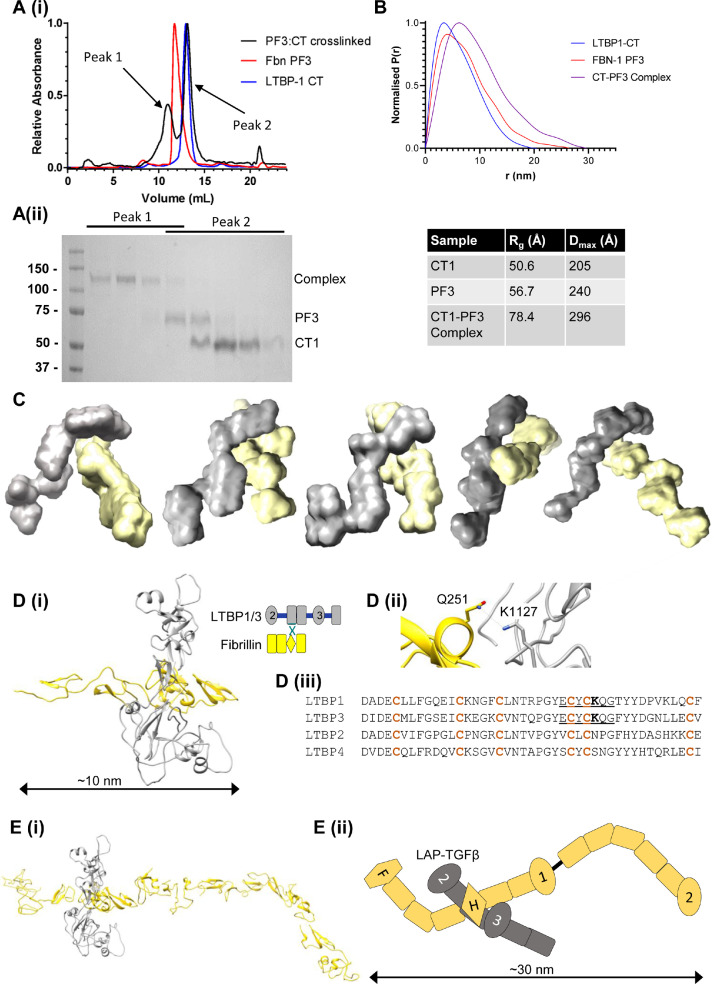
Fig. 5.
Structure of the LTBP1 - fibrillin cross-linked complex. (Ai) The size exclusion chromatography (SEC) profile of PF3 (red) and CT1 (blue) alone and after TG2 treatment (black). After TG2 treatment, a larger species is formed (peak 1). When run on SDS-PAGE (ii), the SEC elutions following TG2 treatment correspond to the CT1-PF3 complex (peak 1) and the two individual components (peak 2). (B) SEC-small-angle X-ray scattering data were collected for CT1, PF3 and the CT1-PF3 complex. The indirect Fourier Transform from the pair distance distribution function shows that PF3 and CT1 are similar in size but the complex is larger. The radius of gyration (Rg) and maximum dimension (Dmax) determined from the experimental SAXS data are indicated. (C) Multiphase modelling shows a perpendicular interface between the two proteins, CT1 (grey) and PF3 (yellow), within the complex. Five representative models are shown. (D(i)) The highest ranked AlphaFold model of the complex between LTBP1 (residues 1021 - 1331) in grey and fibrillin (residues 115 – 287) in yellow showing a perpendicular arrangement. (ii) A close-up view of the proposed region of TG2 crosslinking where K1127 in domain cbEGF13 of LTBP1 is in proximity of Q251 in the hybrid 1 domain of fibrillin. (iii) Sequence alignment shows that this lysine residue is conserved between LTBP1 and LTBP3 but not in LTBP2 and LTBP4. (E(i)) Model of the CT1 region (grey) and fibrillin PF3 region (yellow) based on published SAXS models of CT1 and the fibrillin PF2 region [25,29] and NMR structures of the fibrillin N-terminal region [32,35]. The modelling was informed by the AlphaFold model of the fibrillin-LTBP1 interface. (ii) Cartoon representation of the domain arrangement within the CT1-PF3 complex. H = hybrid domain; F = Fibrillin unique N-terminal region. The TB domains in fibrillin and LTBP1 are numbered.