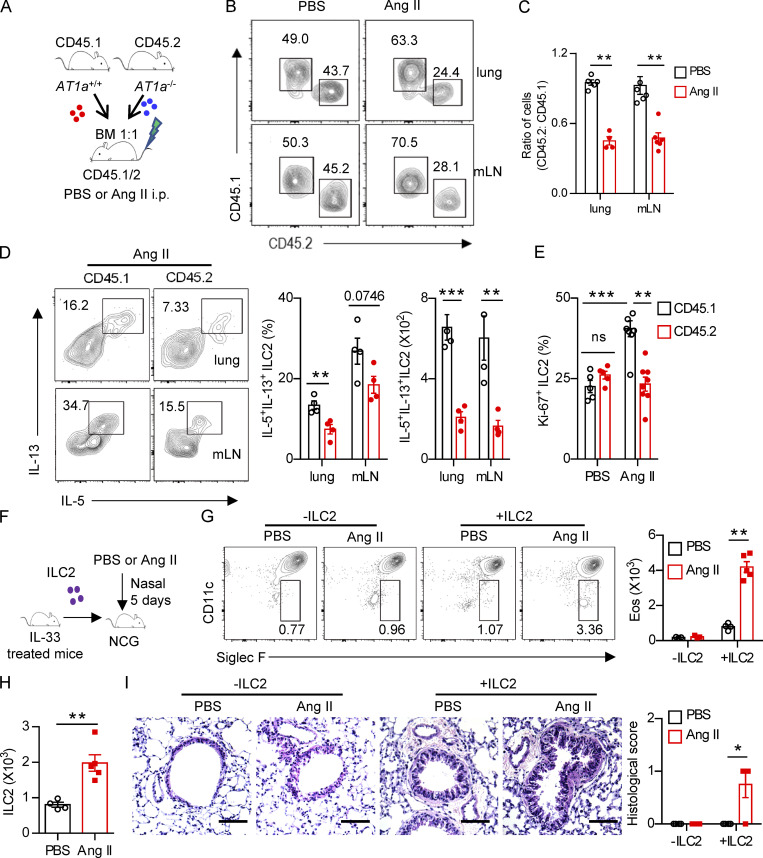
Figure 3.
Regulation of ILC2 by Ang II is cell intrinsic. (A–E) Mixed bone marrow (BM) chimeras were established by transplantation of BM cells from AT1a+/+(CD45.1) and AT1a−/−(CD45.2) mice at 1:1 into irradiated recipient mice (CD45.1/45.2); the recipients were i.p. injected with Ang II or PBS after 6 wk reconstitution. (A) The experimental strategy of mixed BM chimeras. (B and C) The ratio of ILC2s derived from AT1a−/− and AT1a+/+ donor mice (CD45.2: CD45.1) in the lung or mLN. (D) Effector cytokine production of ILC2s derived from donor mice (pregated on CD45.1+ or CD45.2+ cells). ILC2s from lung or mLN were analyzed by flow cytometry after stimulation with PMA, BFA, and ionomycin for 4 h. (E) Proliferation of ILC2s derived from donor mice (pregated on CD45.1+ or CD45.2+ cells). (F–I) Adoptive transfer of ILC2s into NCG mice. Lung ILC2s (2 × 104) from naive mice were injected intravenously into NCG recipients, followed by i.n. administrated with Ang II or PBS for 5 d. NCG mice without ILC2s transfer were used as controls. (F) The experimental strategy of ILC2 transfer. (G) Abundance of eosinophils in BALF of recipients. (H) Absolute counts of lung ILC2s from recipients upon ILC2 transfer and Ang II injection. (I) H&E staining of lung tissues of recipients (scale bar, 100 µm). In all graphs, mean ± SEM is shown. Data are from two independent experiments; n = 4 or 5/group. Two-way ANOVA (C–E, G, and I) or unpaired t test (H) was used. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. Eos, eosinophil.