Figure 1.
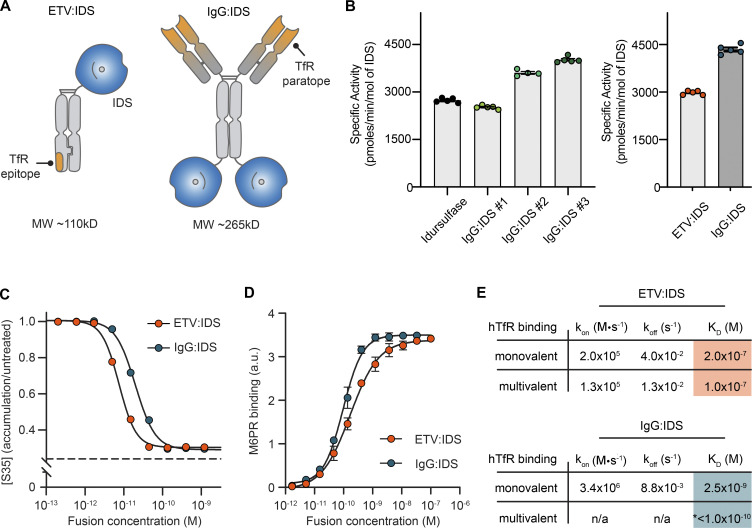
Biochemical characterization of ETV:IDS and IgG:IDS. (A) ETV:IDS is a fusion of the lysosomal enzyme IDS to the TV, a TfR-binding Fc domain. IgG:IDS is a high-affinity anti-TfR huIgG fused to IDS at the C-terminus of each heavy chain. (B) Specific activities of ETV:IDS and IgG:IDS were measured using a synthetic fluorogenic substrate. Graphs display mean ± SD. Samples represented. Left: Idursulfase (commercially approved recombinant IDS), three IgG:IDS preparations generated by cotransfecting CHO cells with increasing amounts of SUMF1 leading to increasing specific activity. Right: ETV:IDS and high-activity IgG:IDS were chosen for further characterization. (C) [35S]sulfate-labeled substrates in MPS II patient-derived fibroblasts after treatment with ETV:IDS or IgG:IDS. n = 3 experiments with three patient lines per phenotype used in each experiment. Dashed line represents the amount of 35S-labeled substrate in healthy control cells. (D) Binding affinities of ETV:IDS and IgG:IDS to M6PR were determined by ELISA; n = 3 technical replicates, representative graph shown. (E) Monovalent affinities and multivalent apparent affinities of ETV:IDS and IgG:IDS to hTfR were measured by surface plasmon resonance. KD, equilibrium dissociation constant; koff, dissociation rate constant; kon, association rate constant. *, the value reported for the multivalent interaction between hTfR and IgG:IDS represents an apparent affinity. n/a, the complex binding kinetics for the multivalent IgG:IDS prevented binding kinetics from being fitted. Graph displays mean values across all experimental replicates ± SEM. a.u., arbitrary unit.