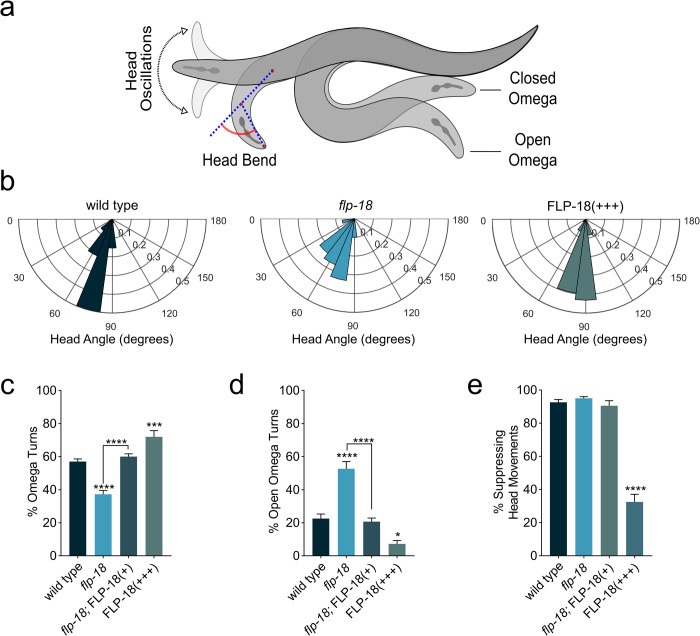
Fig 3. flp-18 mutants are defective in head bending and turning during the escape response.
(A) Schematic depicting head oscillations, ventral turn head angle and open vs closed omega turns. (B) Angle of ventral head bend following touch induced reversal of animals that make omega turns (probability histogram with a bin size of 15°). Each concentric circle represents a probability of 0.1. (C-D) Quantification of omega turning behavior. (C) Percentage of animals that execute omega turns in response to gentle anterior touch. (D) Fraction of open omega turns out of total omega turns. (E) Quantification of the percentage of animals suppressing head oscillations upon gentle anterior touch. Mean ± SEM. significance was calculated using ANOVA with Šidák’s multiple comparison correction (P<0.05 = *, P<0.0005 = ***, P<0.0001 = ****). Sample sizes: Ventral head bend measurement (B) (n = # of animals), wild type (n = 52), flp-18 (n = 30), FLP-18(+++) (n = 58). Suppression of head movement and omega quantification (C-E) (n = # of experiments, 20 worms per experiment) wild type (n = 17), flp-18 (n = 16), flp-18; FLP-18(+) (n = 9), FLP-18(+++) (n = 10).